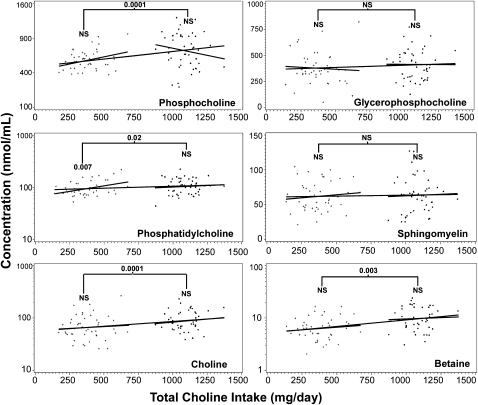
FIGURE 1.
Influence of dietary choline intake on breast-milk choline metabolite concentrations. Pregnant women were enrolled and randomly assigned to receive either a choline supplement (750 mg choline/d) or a placebo (corn oil) from 18 wk gestation to 45 d postpartum. Choline and choline metabolite concentrations were measured by using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry in breast milk collected at 45 d postpartum. Dietary intake was estimated by using 3-d food records and adding the intake from the supplement or placebo. Plots are shown for all 6 metabolites that were measured in breast milk. Regression models with metabolite as the response and total choline intake (diet plus supplement) as the predictor were fitted considering either placebo subjects, supplemented subjects, or all subjects combined (3 solid lines). The following numbers of outliers (defined in Subjects and Methods) for each metabolite were excluded: subjects who received placebo only—glycerophosphocholine (4), phosphocholine (4), phosphatidylcholine (4), sphingomyelin (3), choline (3), and betaine (2); subjects who received the supplement only—glycerophosphocholine (3), phosphocholine (1), phosphatidylcholine (2), sphingomyelin (3), choline (3), and betaine (3); and all subjects combined—glycerophosphocholine (5), phosphocholine (5), phosphatidylcholine (3), sphingomyelin (5), choline (5), and betaine (7). Weighted least-squares regression was performed in the model with breast-milk phosphocholine to overcome heteroskedasticity. To achieve normality, log transformations were made on breast-milk phosphatidylcholine, phosphocholine, betaine, and choline concentrations. Three statistical analyses were performed for each metabolite: effect of intake on concentrations for the placebo group (indicated above the line on the left), effect of intake plus supplement on concentrations for the supplemented group (indicated above the line on the right), and effect of intake plus supplement on concentrations for the combined groups (indicated above the bracket). P values are indicated when differences were significant. Group sizes for the placebo and supplement groups were 46 and 48 subjects, respectively. The R2 values for the placebo, supplement, and placebo plus supplement groups, respectively, are as follows: for phosphocholine—0.11, 0.02, and 0.16; for glycerophosphocholine—0.003, 0.0001, and 0.006; for phosphatidylcholine—0.11, 0.008, and 0.07; for sphingomyelin—0.006, 0.003, and 0.003; for choline—0.008, 0.009, and 0.08; and for betaine—0.005, 0.003, and 0.13. +, subjects randomly assigned to the placebo group; •, subjects randomly assigned to the choline supplement group.