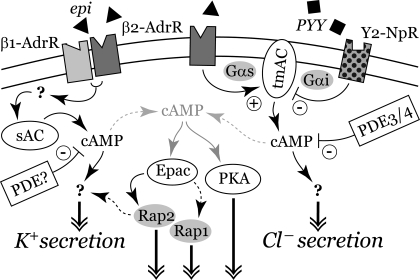
Fig. 12.
Signaling pathways for epi activation of secretion. The β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors (β1-AdrR, β2-AdrR) and Y2-neuropeptide receptor (Y2-NpR) are shown interacting with transmembrane adenylyl cyclase (tmAC) and sAC. Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) limit buildup of the cAMP, leading to activation of secretion. cAMP from other ACs in the cell also is shown leading to PKA activation as well as to Epac activation of Rap1 and Rap2. Activated Rap2 may enter the signaling pathway for K+ secretion, or possibly that for Cl− secretion. cAMP production via the sAC-dependent pathway would be maximally HCO3− sensitive, since the physiological intracellular HCO3− concentration is near the EC50 for sAC (25, 48). Only with severe hypercapnia would CO2 rise sufficiently to stimulate a large increase in cAMP production via the tmAC pathway (66).