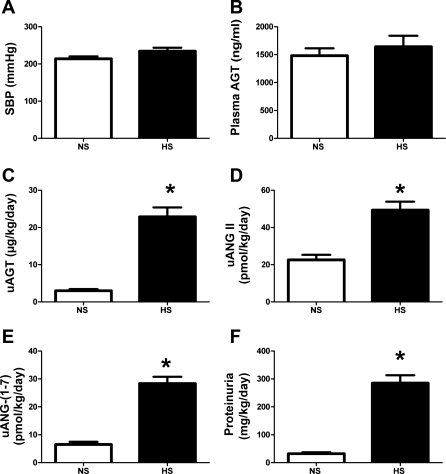
Fig. 1.
Influence of a high-salt (HS) diet on blood pressure, angiotensinogen levels, and other parameters in 15-wk-old male mRen(2).Lewis. A: systolic blood pressure (SBP) in conscious male mRen(2).Lewis congenic rats receiving either normal salt (NS, 1%) or HS (8%) diet were similar as measured by tail cuff plethysmography. B: plasma angiotensinogen levels (ng/ml) were not changed by the HS diet as determined by ELISA. C: urinary angiotensinogen (uAGT; μg·kg−1·day−1) was significantly increased by the HS diet at 15 wk. D: urinary ANG II (uANG II) peptide levels were increased with the HS diet. E: urinary ANG-(1–7) [uANG-(1–7)] levels increased with HS. F: proteinuria was increased with HS. Values are means ± SE; n = 6 rats/group. *P < 0.05 vs. NS males.