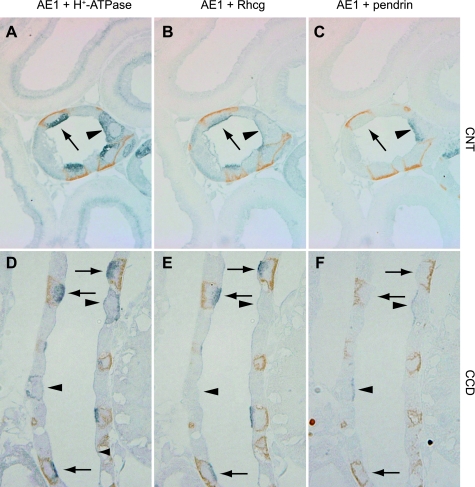
Fig. 2.
Colocalization of Rhcg with intercalated cell-specific markers. A–C: serial sections of adult rat CNT colabeled for AE1 (brown) and H+-ATPase (blue) in A, AE1 (brown) and Rhcg (blue) in B, and AE1 (brown) and pendrin (blue) in C. A-type intercalated cells, identified by apical H+-ATPase, basolateral AE1, and the absence of pendrin immunolabel, express intense Rhcg immunolabel (arrow). Non-A, non-B intercalated cells, identified by apical H+-ATPase, absence of basolateral AE1, and the presence of apical pendrin (arrowhead), express Rhcg immunolabel. D–F: similar studies in the CCD. Again, A-type intercalated cells identified by apical H+-ATPase, basolateral AE1, and the absence of apical pendrin express Rhcg immunolabel (arrows). In contrast to the non-A, non-B intercalated cell, B-type intercalated cells, identified by basolateral H+-ATPase and apical pendrin immunolabel (arrowheads), do not express detectable Rhcg immunolabel.