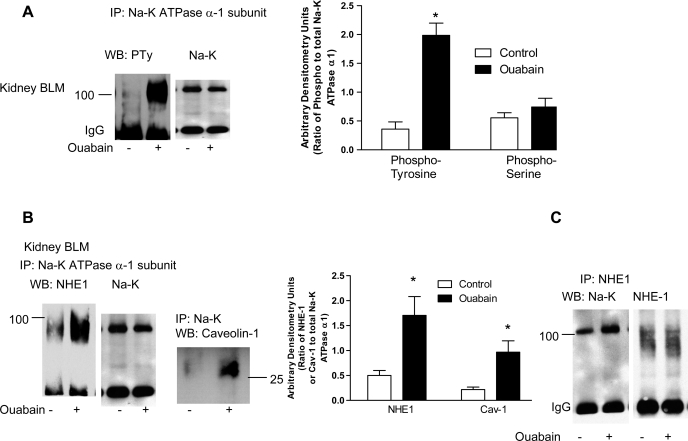
Fig. 3.
Effect of nanomolar ouabain on Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit phosphorylation and association with NHE-1 in kidney BLM. Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing 200–250 g, were treated for 4 days intraperitoneally with ouabain (1 μg·kg body wt−1·day−1). Kidneys were removed on day 4, decapsulated, and the cortex was carefully separated from the medulla. BLM were prepared from whole cortex as described in experimental procedures. Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit (A and B) or NHE-1 (C) was immunoprecipitated (IP) as described in experimental procedures. Immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using phosphotyrosine or phosphoserine (A), NHE-1 or caveolin-1 (B), or Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit (C) antibodies. The blots were stripped and analyzed by immunoblotting for Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit (A and B) or NHE-1 (C) for equal loading. Each bar represents data as AU (ratio of phosphotyrosine or phosphoserine to total Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit or Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit or NHE-1 to total NHE-1 or Na-K-ATPase α1-subunit immunoprecipitated); values are means ± SE from 8 BLM preparations from different animals (n = 8). *P < 0.05 by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni analysis.