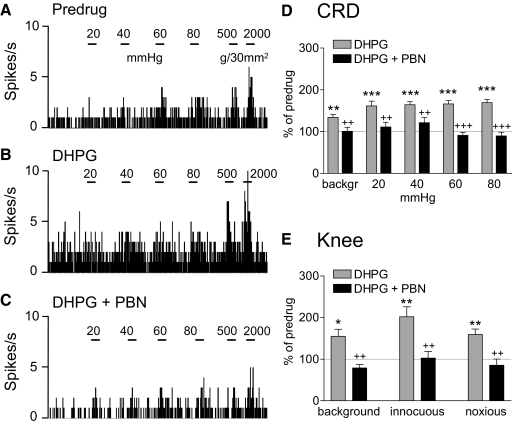
Fig. 6.
ROS scavenger phenyl-N-t-butyl nitrone (PBN) inhibits DHPG-induced facilitation. A–C: background activity and evoked responses of an individual CeLC neuron before drug application (predrug, A), during administration of DHPG (100 μM, concentration in microdialysis probe; 15 min) into the CeLC (B), and during coapplication of DHPG and PBN (100 mM; 15 min; C). Same display as in Fig. 4. PBN inhibited the facilitatory effects of DHPG on responses to CRD and knee joint stimulation. D and E: bar histograms (mean ± SE) show background activity and responses evoked by CRD (n = 6 neurons; D) and by knee joint compression (n = 5 neurons; E) normalized to predrug control (set to 100%). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (compared with predrug control); ++P < 0.01, +++P < 0.001 (compared with DHPG; Tukey's multiple comparison test).