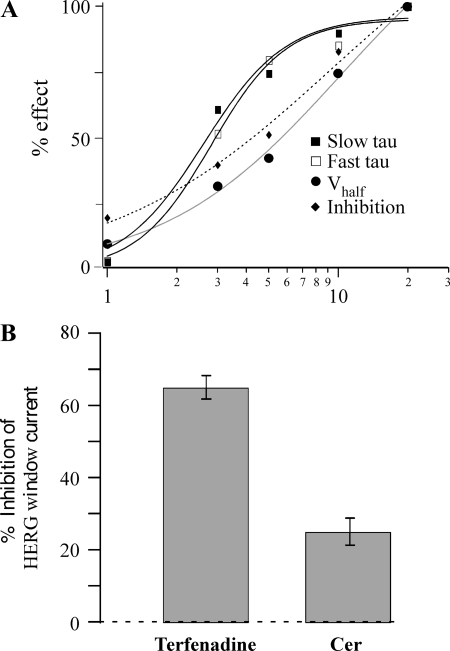
Fig. 4.
IHERG is affected by physiological ceramide concentrations. A: dose-response relationships for the effect of Cer on slow and fast τ, V1/2, and inhibition. The %effect values were normalized to effect measured at 20 μM Cer. The smooth lines are fits to the data using the Hill equation to yield EC50 values of 2.6, 2.8, 10.2, and 9.4 μM, and Hill coefficient values were 2.4, 2.7, 1.1, and 0.9 for fast τ, slow τ, V1/2, and inhibition, respectively. The applied Cer concentrations were 1, 3, 5, 10, and 20 μM (n = 3, 3, 8, 8, and 6, respectively). B: Cer inhibits HERG window current. The holding potential was set to the voltage (usually −20 mV) generating maximum window current, which was measured before, during, and upon recovery from 10 μM Cer (n = 5). To confirm that HERG channels produced the window current, inhibition by a known HERG blocker, terfenadine (0.1 μM), is also presented (n = 5).