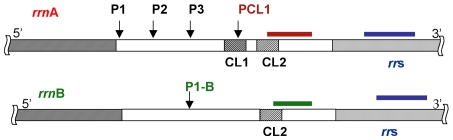
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the two rrn operons of M. fortuitum.
Each operon comprises, in the order 5′ to 3′, the genes for 16S rRNA (rrs), 23S rRNA (rrl) and 23S rRNA (rrf). The 5′-end of the operon is presented. Horizontal bars indicate the regions of the transcripts analyzed using qRT-PCR: rrs (mature 16SrRNA) (blue); rrnA operon PCL1 (red) and rrnB operon P1-B (green). The detection of rrnA PCL1 includes all transcripts derived from all the four rrnA promoters (namely, P1 to P3 and PCL1). The rate ε rrs nucleotides h−1 of 16S rRNA synthesis was calculated by means of equation (6). The analysis is based on two assumptions; first, that there is one precursor-16S rRNA per RNAP [34]; and secondly, that the synthesis of precursor-16S rRNA is completed before the synthesis of precursor-23S rRNA begins [33].