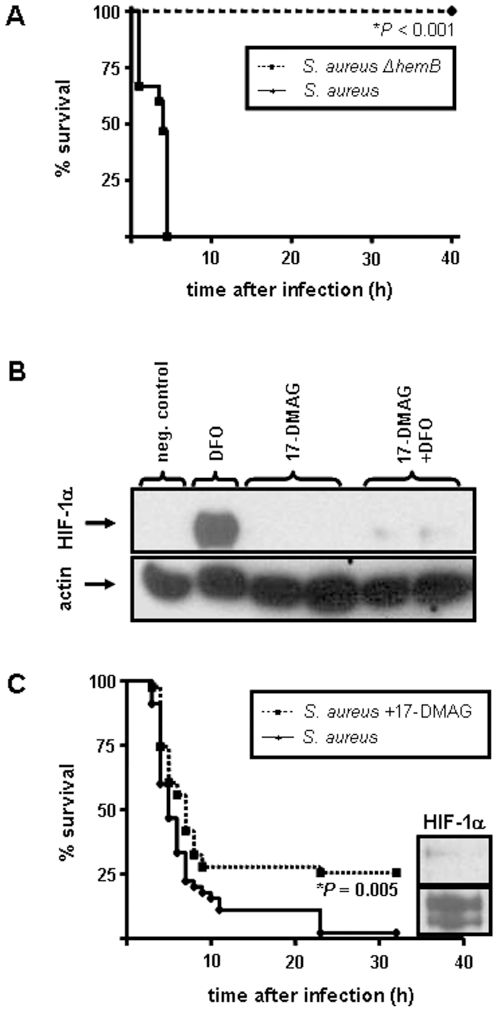
Figure 9. Role of HIF-1 in infections with S. aureus in a murine peritonitis model.
(A) Survival of NMRI mice after intraperitoneal infection with S. aureus (wt; S. aureus 8325-4; n = 8) or S. aureus ΔhemB (SCV, S. aureus ermΩhemB 8325-4; n = 8). Note the higher susceptibility of mice infected with S. aureus 8325-4 compared to the mice infected with S. aureus ΔhemB. *significant difference: P<0.001. (B) Inhibition of DFO induced HIF-1 activation in HeLa-229 cells by 17-DMAG. Cells were incubated with 17 DMAG (10 µmol/L) for 16 hours following induction of HIF 1 activation by the iron chelator DFO (200 µmol/L) for six hours. HIF 1α protein was analyzed in Western blots (loading control: actin). Negative control: uninfected cells. (C) Survival rate of NMRI mice after intraperitoneal infection with S. aureus (S. aureus 8325-4). One group of mice was treated 24 h and 16 h before infection with the HIF-1 inhibiting compound 17-DMAG (25 mg/g body weight). Note the higher survival rate of 17-DMAG-treated mice (n = 45) compared with control mice (n = 45). *significant difference: P = 0.005 (Kaplan-Meier analysis).