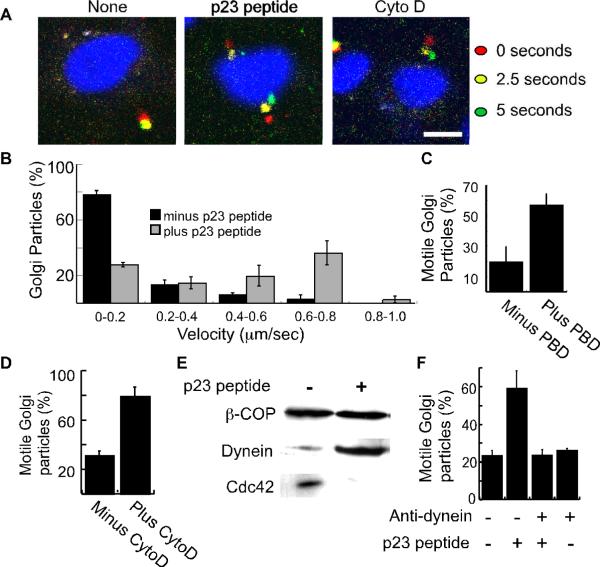
Figure 6. p23 peptide, recombinant PBD, and cytochalasin D stimulate dynein-dependent Golgi motility.
(A) Shown are merged images of confocal micrographs taken at an initial time point (0 seconds; red), 2.5 seconds (yellow), and 5 seconds (green) after incubating rat-liver Golgi membranes with permeabilized NRK cells. Prior to their addition to the NRK cells, the membranes were incubated with p23 peptide or cytochalasin D as indicated. Nuclei were labeled with 10 μM DRAQ5. The bar represents 10 μm. (B) Golgi membranes were treated with or without the p23 peptide and incubated with permeabilized cells. The velocities of Golgi particles was calculated and plotted as a histogram representing the average from 3 independent experiments. A total of 109 particles associated with 53 cells (minus peptide) and 65 particles associated with 54 cells (plus peptide) were analyzed. The standard error is indicated by bars. (C) The fraction of motile Golgi particles during a five second interval was determined for recombinant PBD (5 μg/ml) or mock-treated membranes. Over three independent experiments, 56 Golgi particles associated with 45 cells (minus PBD) and 54 particles associated with 48 cells (plus PBD) were analyzed. PBD treatment significantly increased the fraction of motile membrane particles (p<0.04). (D) The fraction of motile Golgi membranes was determined following mock or cytochalasin D (CytoD) treatment. Over three independent experiments, 226 Golgi particles associated with 77 cells (minus CytoD), and 273 particles associated with 59 cells were analyzed. The standard error is indicated by bars. Cytochalasin D significantly increases the fraction of motile particles (p<0.05). (E) Rat-liver Golgi membranes were incubated using reaction conditions identical to those used for the motility assay shown in panels A-D. Following the incubation, the Golgi membranes were reisolated by centrifugation and processed for SDS-PAGE. Western blot analysis was used to determine the levels of β-COP, dynein, and Cdc42 as indicated. (F) The fraction of motile Golgi membrane particles was determined after mock treatment (176 particles associated with 100 cells), treatment with the inhibitory dynein antibody 70.1 (199 particles; 114 cells), treatment with the p23 peptide (235 particles; 123 cells), or treatment with both (206 particles; 130 cells). Plotted are the averages from three independent experiments. The standard error is indicated by bars. The anti-dynein antibody significantly inhibits p23-stimulated motility (p<0.05).