Fig. 4.
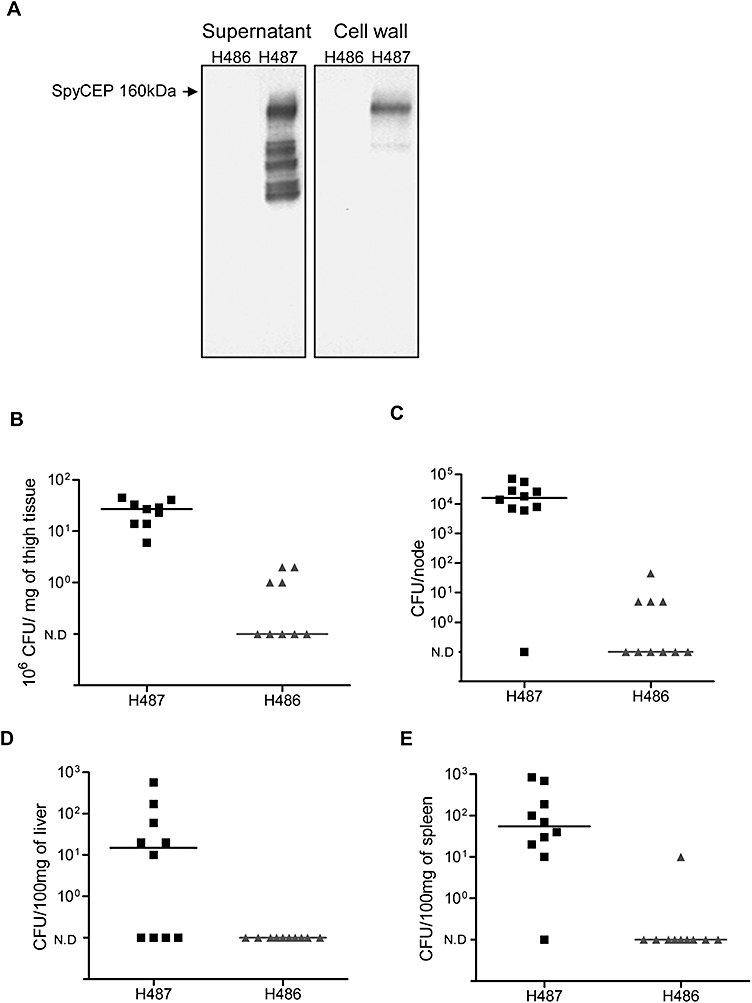
Heterologous expression of SpyCEP in L. lactis is sufficient to resist bacterial clearance and promote dissemination. A. Heterologous expression of SpyCEP by L. lactis strain H487 and parental control L. lactis strain H486. Western blots for SpyCEP were performed on culture supernatants (left panel) and cell wall preparations (right panel). H487 produced SpyCEP in both supernatant and cell wall. Lower molecular weight bands represent autocatalytic cleavage of SpyCEP. B. Bacterial quantification in muscle tissue demonstrating heavy growth in mice infected with SpyCEP-expressing L. lactis strain H487 compared with control strain H486 (P = 0.0001). C. Bacterial dissemination of L. lactis to regional lymph node. Quantification of bacteria in each inguinal lymph node shows greater bacterial spread to node in mice infected with H487 compared with H486 (P = 0.0015). D. Bacterial quantification in liver. SpyCEP was also essential for systemic spread of L. lactis to liver with greater bacterial burden in liver of mice infected with H487 compared with H486 (P = 0.012). E. Bacterial quantification in spleen with greater bacterial burden in spleen of mice infected with H487 compared with H486 (P = 0.0003). n = 10 per group representative of two experiments. ND, not detected; cfu, colony-forming units; horizontal line, median.
