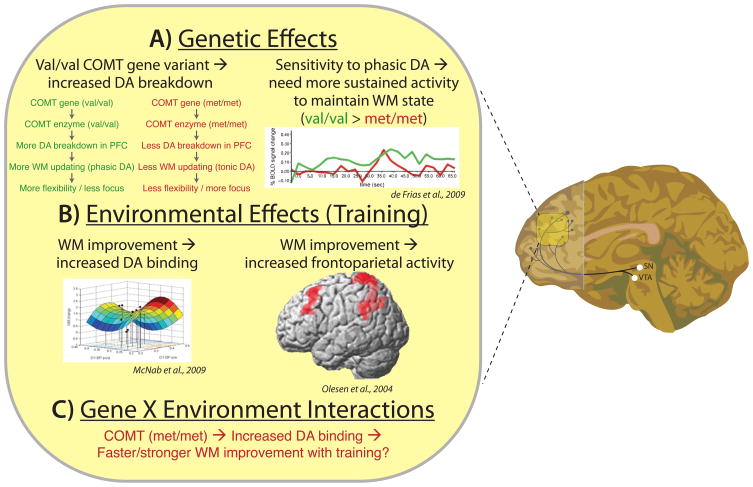
Figure 3. Explaining individual variation in PFC function: An example of how neural mechanisms can bridge the gap between genetic/environmental factors and individual differences.
A) PFC activity covaries with the COMT val158met variant (on right) [52]. One explanation for this correlation involves the differential breakdown of dopamine in PFC across val (more breakdown) and met (less breakdown) genotype variants (on left). B) PFC dopamine receptor binding (left) and PFC activity during a WM task (right) are modulated by practice performing particular WM tasks [66,67], suggesting that frequently performed day-to-day tasks (e.g., frequently dialing phone numbers from memory) may affect PFC function, which in turn may increase WM capabilities. C) Further research is necessary to establish clear gene X environment interactions between COMT variants, PFC function, and individual differences in behavior. We suggest that the met variant, which involves slower breakdown of DA, may promote an increase in DA receptor binding (and a possible increase in DA receptors) to allow for faster/stronger increases in WM capacity with practice.