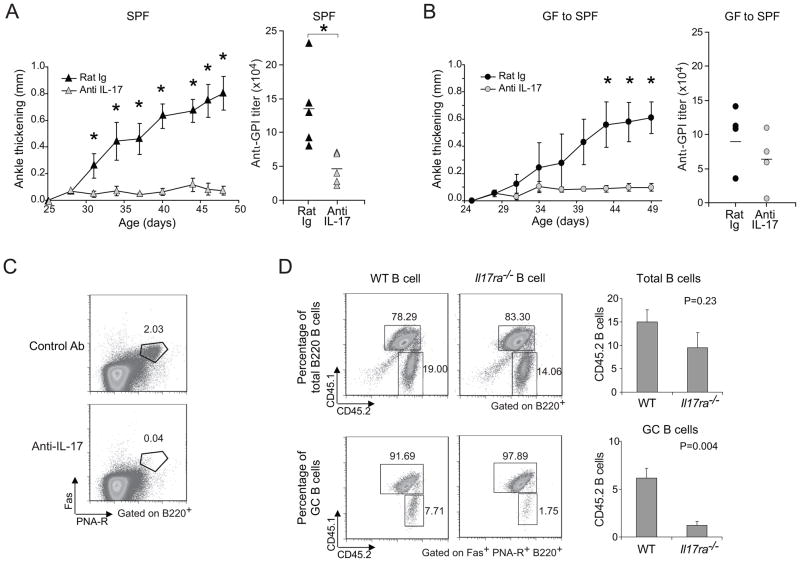
Figure 4. Reduction of arthritis by neutralization of IL-17.
(A) 25-day-old SPF K/BxN mice were treated with 100μg of anti-IL-17 or control rat IgG every 3 days, and ankle thickening was measured over time (left panel). Mean ± s.e of the two groups (n=5 in both groups from two independent experiments is plotted; Asterisks indicate statistical significance using the Student s t-Test, *P<0.05.). Sera were collected at the end of the experiment, and anti-GPI titers quantified (right panel). Symbols represent individual mice; bar indicates the mean. (B) At 23 days of age, GF mice were transferred to our SPF facility, and were treated with 100μg anti-IL-17 or control rat IgG every 3 days from day 24. Otherwise as in the A panels (n=4 in both groups from one experiment; Asterisks indicate statistical significance using the Student s t-Test, *P<0.05). (C) SPF K/BxN mice were treated as in panel A. At the end of treatment, splenocytes were isolated and stained with Abs recognizing B220, CD4 or Fas, or with PNA, and were analyzed by flow cytometry, gating as indicated. Values represent the percentages of Fas+PNA-R+ cells in total B cells. Data are representative of two independent experiments with two mice per group. (D) B cells from either WT or Il17ra−/− mice were combined with splenocytes from arthritic K/BxN mice and transferred into BxN.Rag1−/− recipients. The origins of B cells were identified by expression of the congenic marker: CD45.1+CD45.2+ for K/BxN B cells and CD45.2 for Il17ra−/− or WT B cells. Percentages of K/BxN B cells and Il17ra−/− or WT B cells among total B cell or GC B cell populations are indicated. The quantitative data of Il17ra−/− or WT B cell percentage among total B cells and GC B cells were also shown as mean + s.e. (n=4, data combined from two independent experiments).