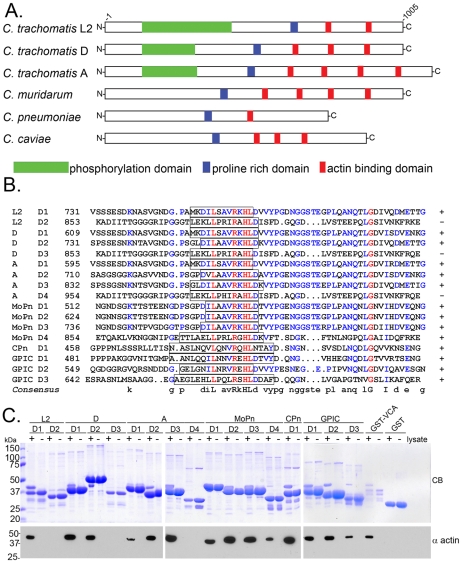
Figure 3. Tarp orthologs harbor multiple actin binding domains.
A) A schematic of the Tarp orthologs from C. trachomatis serovar L2 (L2), C. trachomatis serovar D (D), C. trachomatis serovar A (A), C. muridarum (MoPn), C. pneumoniae (Cpn), and C. caviae (GPIC) indicating the location of the putative actin binding domains (red boxes), a proline rich domain (blue boxes), and tyrosine rich phosphorylation domain (green boxes). B) ClustalW sequence alignment of the putative actin binding domains from Tarp orthologs in A. The sequence predicted to harbor the actin binding alpha helix is indicated by the open box. Identical amino acids within each alignment are in red. Similar residues are in blue. The consensus sequence shown is based on homology greater than 50%. The number indicates the amino acid residue of the amino terminus of the peptide shown. C) The Tarp orthologs associate with actin. GST-fusions of the Tarp orthologs described above harboring sequence similar to the C. trachomatis L2 (L2) actin binding domain were expressed and purified. Extracts from HeLa cells were incubated with GST or GST fusions to Tarp orthologs and specifically bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining (CB). Samples identical to those shown in the Coomassie-stained gel were subject to immunoblotting with an actin (α actin) specific antibody. A GST fusion to the VCA domain of N-wasp (GST-VCA) served as a positive control for actin binding.