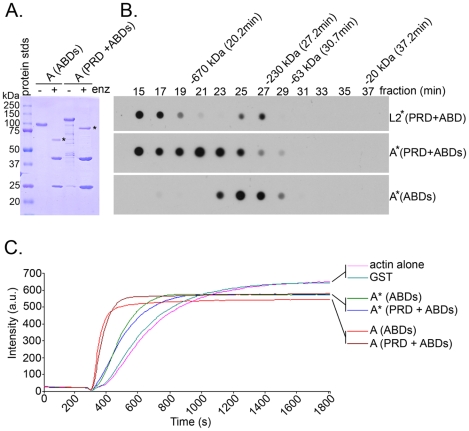
Figure 5. The C. trachomatis serovar A Tarp ortholog employs a spire-like actin nucleation mechanism and does not require the L2 Tarp proline rich domain for actin nucleation.
C. trachomatis serovar A Tarp fragments harboring either the three functional actin binding domains (ABDs) alone or the actin binding domains and the proline rich domain (PRD) were digested to remove the GST moiety and analyzed by gel filtration and pyrene actin polymerization assays. A) C. trachomatis serovar A GST-Tarp fusion proteins were purified and digested with protease (+/− enz) to remove the GST moiety (* indicates GST is removed). Proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. B) Removal of the proline rich domain from C. trachomatis A Tarp inhibits oligomerization. Gel filtration of proteins shown in panel A. Protein fractions were collected in 2-min intervals from gel filtration columns and immobilized to a nitrocellulose membrane by vacuum filtration. Membranes were subjected to immunoblotting with a Tarp specific antibody. Protein standards are indicated above the dot-blot with respective molecular weight and peak elution times. C) Oligomerization of C. trachomatis A Tarp is not required for actin nucleation. Purified Tarp (A) with and without proline rich domain increased actin polymerization compared to GST and actin alone controls in pyrene actin polymerization assays. The results are from one experiment representative of three separate experiments.