Figure 3.
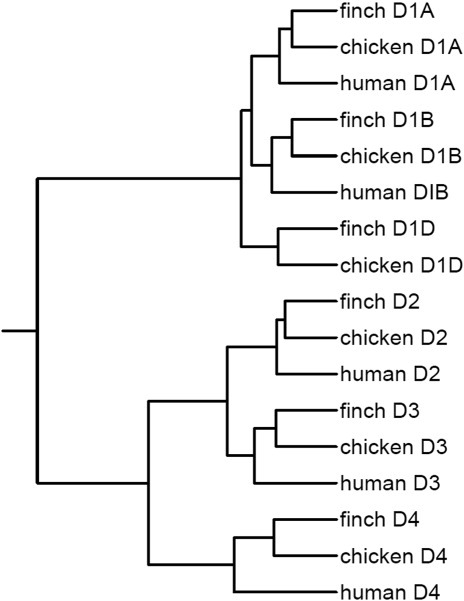
Phylogenetic analyses of dopamine receptors in the zebra finch, chicken, and human. Shown is a phylogram generated with the full-length protein coding sequences (Supp. Info. Fig. 1), the dialign alignments (http://bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/dialign/submission.html), and the iTOL tree-generating software (http://itol.embl.de/). For D2 and D3, variant 1 sequences were used. Branch lengths represent evolutionary time separating gene relationships (longer branch, more time). The D1 family has shorter branch lengths, indicating that they are probably more closely related than the D2 family. All receptor types show closer homologies to each other across species than they do to other receptor types within species.
