Figure 3.
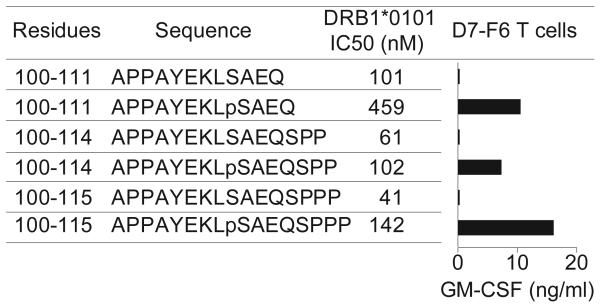
Specific recognition of phosphorylated versus non-phosphorylated MART-1 peptides by CD4+ T cells. The phospho-MART-1-specific T cell clone D7-F6 was co-incubated overnight with HLA-DR1+ 2048-EBV cells pre-pulsed with peptides (25 μM). GM-CSF secretion was measured by ELISA. Background GM-CSF secretion from T cells + APC + HA307-319 control peptide was <15 pg/ml. Results are representative of four separate experiments with D7-F6 and the parent T cell line D7 showing specific T cell recognition of phosphopeptides but not non-phosphorylated peptides, despite the comparatively lower MHC affinities (higher IC50 values) of the phosphorylated MART-1 peptides.
The oligoclonal pMART-1-specific CD4+ T cell line designated “D7” was raised by repetitive in vitro stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from a melanoma patient expressing HLA-DRβ1*0101. Briefly, T cells were grown under microculture conditions and stimulated every 10–14 days with irradiated autologous PBMC or HLA-DR1+ allogeneic EBV-B cells pulsed with pMART-1100-111 (APPAYEKLpSAEQ). Long-term CD4+ T cell cultures were maintained in RPMI 1640 + 10% heat-inactivated human AB serum, IL-2 120 IU/ml, and IL-7 and IL-15 at 25 ng/ml each. The T cell clone designated “D7-F6” was subcultured from D7 T cells under limiting dilution conditions in microtiter plates, and stimulated repetitively with pMART-1100-115 (APPAYEKLpSAEQSPPP). To assess T cell recognition of peptides, 1.2–5 × 104 T cells/well were co-cultured overnight in flat-bottom 96-well plates with 1 × 105 HLA-DR1+ EBV-B cells which had been pre-pulsed with peptides. Medium consisted of RPMI 1640 + 10% human AB serum, with IL-2 120 IU/ml. Culture supernatants were harvested, and GM-CSF and IFN-γ secretion by activated T cells was measured using commercially available ELISA kits (R&D Systems). Competition assays to quantitatively measure peptide binding to HLA-DRβ1*0101 were based on inhibition of binding of a high affinity radiolabeled peptide to purified MHC molecules.33 HLA class II molecules were purified from the EBV-transformed homozygous B lymphoblastoid cell line LG2. Peptide binding assays were performed by incubating purified human class II molecules (5–500 nM) with various concentrations of unlabeled peptide inhibitors and 0.1–1 nM 125I-radiolabeled probe peptide for 48 h in PBS containing 0.05–0.15% Nonidet P-40 and a protease inhibitor cocktail.15,33 MHC binding of the radiolabeled peptide (HA307–319; PKYVKQNTLKLAT) was determined by capturing peptide–MHC complexes on L243 (anti-HLA-DRA) antibody coated Lumitrac 600 plates (Greiner Bio-one) and measuring bound cpm. The concentration of peptide yielding 50% inhibition of the binding of the radiolabeled probe peptide (IC50) was then calculated. Peptides were typically tested at six different concentrations covering a 100,000-fold dose range, and in three or more independent assays. Under the conditions utilized, where [label] < [MHC] and IC50 ≥ [MHC], the measured IC50 values are reasonable approximations of the KD values.15