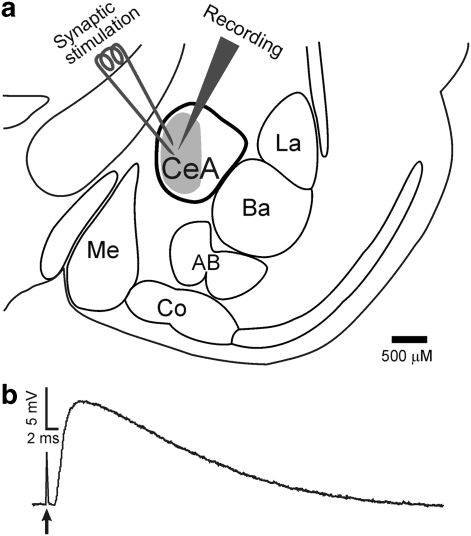
Figure 1.
Synaptic stimulation and recording in the amygdale. (a) Schematic of the amygdala and its related nuclei. The recording electrode was placed in the medial subdivision (gray area) of the central nucleus, and the stimulation electrode used to elicit synaptic responses was placed near the recording site. CeA: central nucleus; La: lateral nucleus; Ba: basal nucleus; AB: accessory basal nucleus; Co: cortical nucleus; Me: medial nucleus (Sah et al, 2003). (b) Representative recording of an IPSP elicited upon delivery of a single electric stimulation (stimulation artifact denoted by arrow). The synaptic response developed <2 ms after stimulation, consistent with a monosynaptic response. The superfusate always contained CNQX, APV, and CGP55845A to block AMPA, NMDA, and GABAB receptors, respectively.