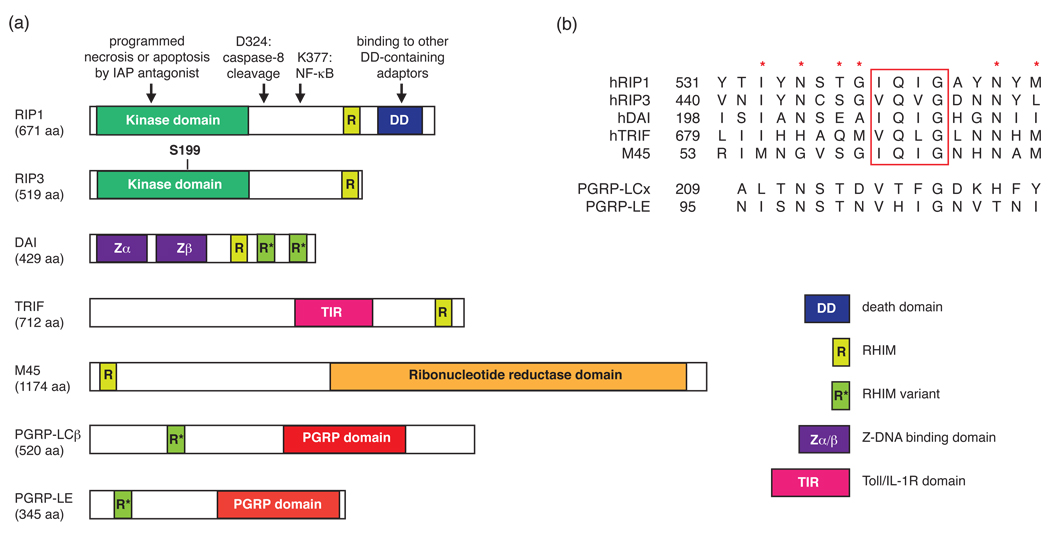
Figure 1. The emerging family of RHIM-containing proteins.
(a) Schematic diagram of human, viral and Drosophila adaptor proteins containing RHIMs. The arrows indicate the amino acid residues and domains important for RIP1 function. S199 is a reported necrosis-specific phosphorylation target site on RIP3 [28]. (b) Sequence alignment of the RHIM or RHIM-like domains. The red rectangle denotes the highly conserved (I/V)Q(I/V/L)G tetrapeptide found in the RHIM. The red asterisks represent other highly conserved residues within the RHIM domain. The numbers represent the amino-terminal boundary of the listed sequences.