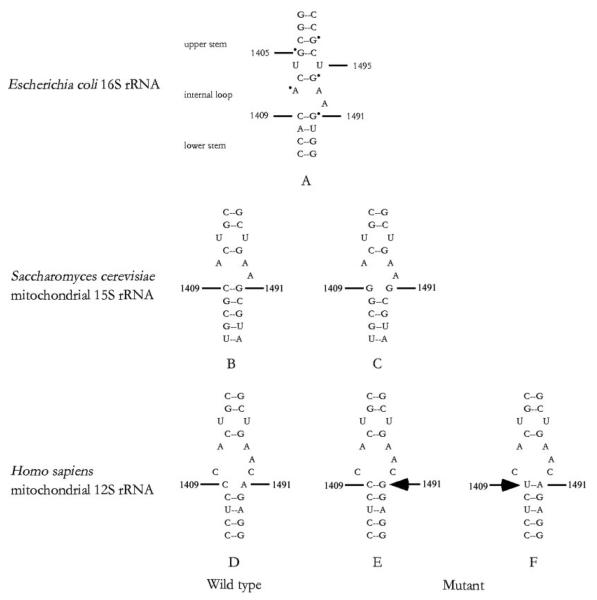
Fig. 1. Secondary structure of the decoding site of small ribosomal RNAs.
A, the A-site of the E. coli 16 S rRNA oligonucleotide showing the dimethyl sulfate footprints, observed in the presence of the aminoglycosides neomycin or paromomycin, is marked with a dot (10, 11). The corresponding region of S. cerevisiae mitochondrial 15 S rRNA and human mitochondrial 12 S rRNA is shown as the wild type version (B and D) and in the version containing the C1409G (nt 1477 in yeast 15 S rRNA) (C), A1491G (nt 1555 in human 12 S rRNA) (E), and C1409T mutations (nt 1494 in human 12 S rRNA) (F), respectively.