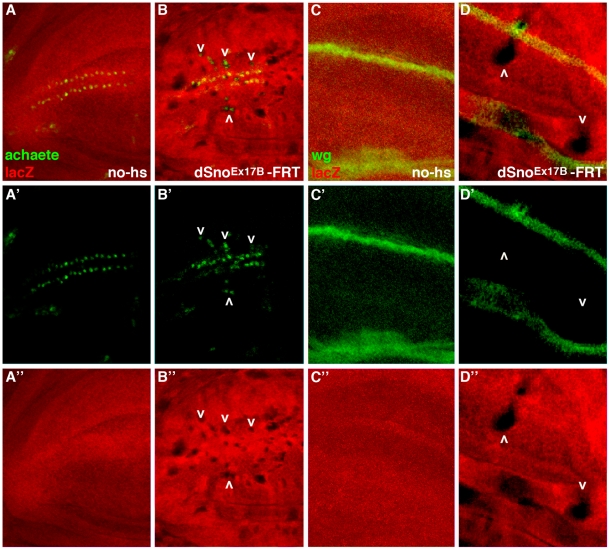
Figure 1. dSno clones in the wing generate ectopic expression of a Wg target gene but do not affect Wg expression.
dSnoEx17B FRT40A/Arm-lacZ FRT40A third instar wing disk with a focus on the wing pouch and anterior margin primordia. (A, A', A”) Disk without heat shock stained with anti-Ac (green) and anti-lacZ (red) shown merged and as individual channels. Arm-lacZ is ubiquitously expressed. (B, B', B”) Disk with hs-FLP-induced dSno mutant clones. Clones of cells homozygous for dSnoEx17B are seen via the absence of lacZ. Loss of dSno does not affect normal nuclear Ac expression and numerous mutant clones outside this area within the anterior compartment display ectopic Ac expression (arrowheads). (C, C', C”) Disk without heat shock stained with anti-Wg (green) and anti-lacZ (red). (D, D', D”) Disk with hs-FLP-induced dSno mutant clones. Loss of dSno does not affect normal Wg expression and mutant clones outside this area, in either the anterior or posterior compartment, do not display ectopic Wg (arrowheads). Clones at the anterior-posterior compartment boundary that encompass both cell layers and bisect the Wg stripe appear to support increased Wg diffusion into the ventral but not the dorsal compartment (n = 6).