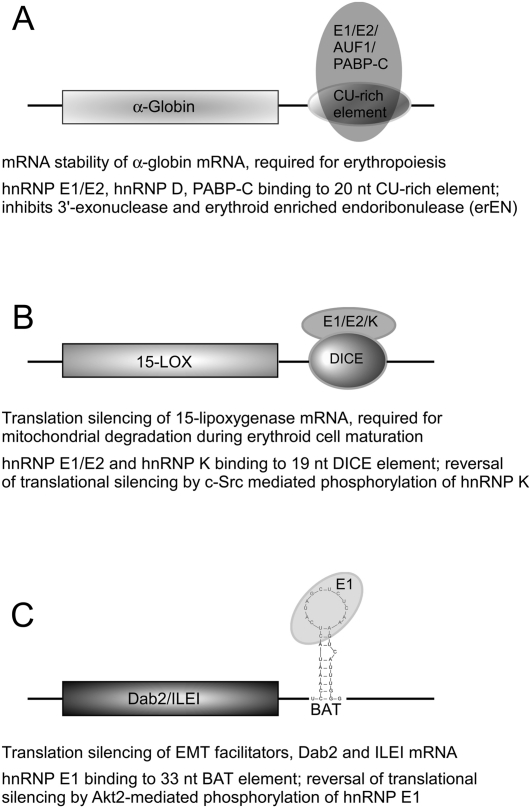
FIGURE 2.
Post-transcriptional regulation by hnRNP E1 during development and differentiation. hnRNP E1 alone, or in combination with other hnRNPs, modulates mRNA stability of α-globin (A) or the translation of 15-LOX (B) or Dab2 (C) mRNAs. The regulatory mechanism involves binding to putative cis elements in the 3′-UTRs, which in most cases is disrupted by phosphorylation of one or more of the bound hnRNP proteins. A brief description of each regulatory mechanism is given. (15-LOX) 15-lipoxygenase; (DICE) differentiation control element; (BAT) TGFβ-activated translation element; (Dab2) disabled-2; (ILEI) interleukin-like EMT inducer.