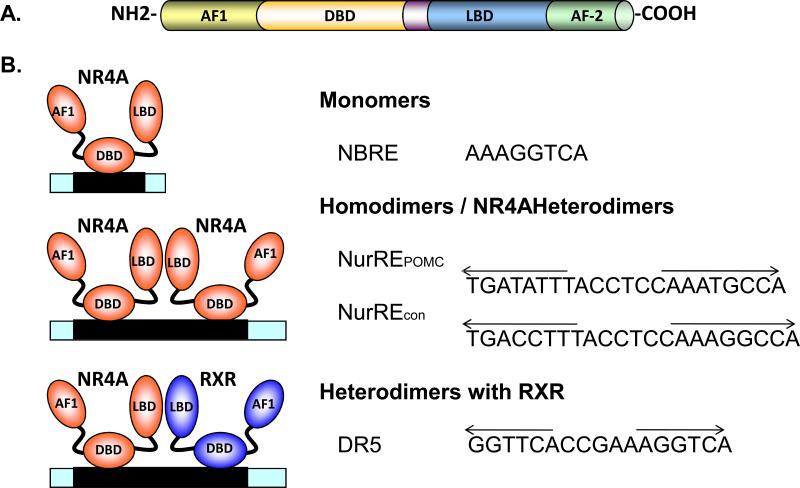
Figure 1. Molecular biology of NR4A orphan nuclear receptors.
NR4A receptors share the conserved molecular structure consisting of a N-terminal AF-1 domain, the central DNA-binding domain (DBD) and C-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD) and the AF-2 domain (Panel A). NR4A receptors induce gene expression by binding as monomers to the NBRE site and as homodimers or heterodimers to the NurRE site in the promoter of their regulated target genes. NurREPOMC represents the binding sequence demonstrated in the pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) promoter, while NurRECON represents the NurRE site comprising consensus NBRE sites. Nur77 and Nurr1, but not NOR1, heterodimerize with RXR and bind to the direct repeats of nuclear receptor binding motif separated by five nucleotides (DR5) (Panel B).