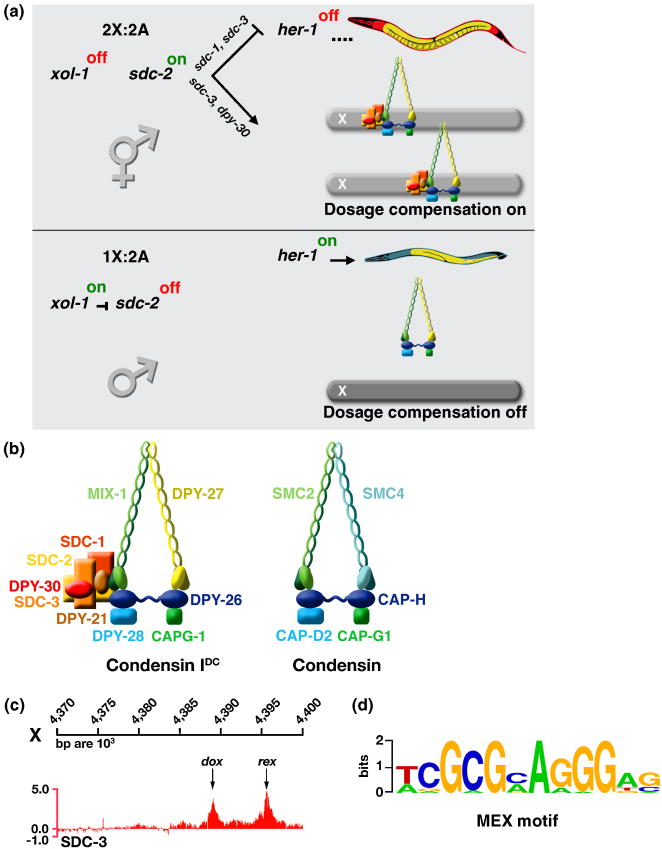
Figure 2. Regulation of Dosage Compensation in C. elegans.
(a) Partial genetic pathway for sex determination and dosage compensation. In XX embryos, xol-1 is repressed by the double dose of XSEs, permitting the XX-specific protein SDC-2 to activate dosage compensation and to repress her-1, a male-specific sex determination gene. SDC-2 acts with SDC-3 and DPY-30 to recruit the DCC condensin subunits to X. SDC-2 acts with SDC-1 and SDC-3 to repress her-1. SDC-2 plays the lead role in recognizing X sequences, while SDC-3 predominates in recognizing the SDC binding sites at her-1. In XO embryos, ASEs overcome XSEs to activate xol-1, resulting in sdc-2 repression and her-1 activation, thereby setting the male sexual fate. The DCC is not loaded onto X.
(b) The DCC consists of five condensin-like components (DPY-27, MIX-1, DPY-26, DPY-28, and CAPG-1) that are homologous to canonical condensin subunits SMC2, SMC4, CAP-H, CAP-D2, and CAP-G1, respectively The DCC also contains at least five additional factors that confer X- and sex-specificity (SDC-2, SDC-3, and DPY-30) or assist in repression (DPY-21 and SDC-1).
(c) DCC binding sites have been mapped by ChIP chip experiments and classified into two categories based on their ability to bind the complex when detached from the X chromosome. rex sites (recruitment elements on X) bind the complex robustly when they are detached from X and present either in multiple copies on extrachromosomal arrays (see Figure 3a) or in low copy number integrated onto an autosome. dox sites (dependent on X) fail to bind the DCC when detached; they depend on the broader X chromosomal context for their ability to associate with the DCC.
(d) Motif searches identified a twelve base pair consensus motif that is enriched at rex sites relative to dox sites and on X chromosomes relative to autosomes. Mutations within the motif disrupt the ability of rex sites to recruit the DCC (see Figure 3a).