FIGURE 1.
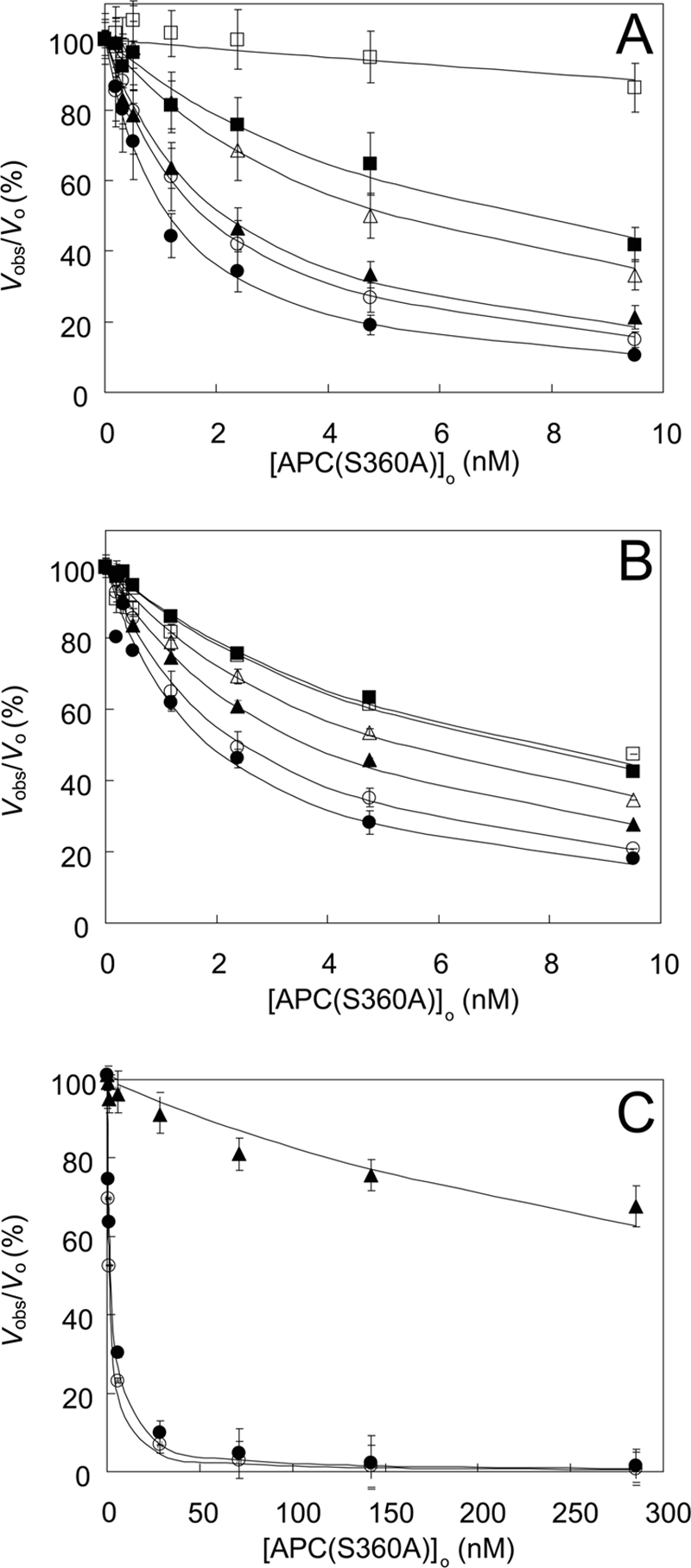
Inhibition of prothrombin activation by APC(S360A). Shown are the effects of FXa and prothrombin in the presence of Arg506 and Arg306 cleavage sites in FVa. A, effect of varying APC(S360A) concentrations on prothrombin activation by 7.2 pm FVa, 40 μm phospholipid vesicles (10:90, DOPS:DOPC), 3 mm CaCl2, 1 μm prothrombin, and 25 (●), 50 (○), 100 (▴), 250 (▵), 500 (■), and 5,000 (□) pm FXa. B, effect of varying APC(S360A) concentrations on prothrombin activation by 7.2 pm FVa, 40 μm phospholipid vesicles (10:90, DOPS:DOPC), 3 mm CaCl2, 50 pm FXa, and 0.5 (●), 1.0 (○), 2.5 (▴), 5 (▵), 10 (■), and 20 (□) μm prothrombin. C, effect of varying APC(S360A) concentrations on prothrombin activation by 7.2 pm wild type FVa (●), FVa Q306R506Q679 (○), or FVa R306Q506Q679 (▴), 40 μm phospholipid vesicles (10:90, DOPS:DOPC), 3 mm CaCl2, 1 μm prothrombin, and 50 pm FXa. Initial rates of prothrombin activation at varying APC(S360A) concentrations are presented as fractions (%) of the rate in the absence of APC(S360A) (vobs/vo). Indicated are the averages ± S.E. from two different experiments. The solid lines represent the hyperbolic fits of the data. Further experimental conditions are described under “Experimental Procedures.”
