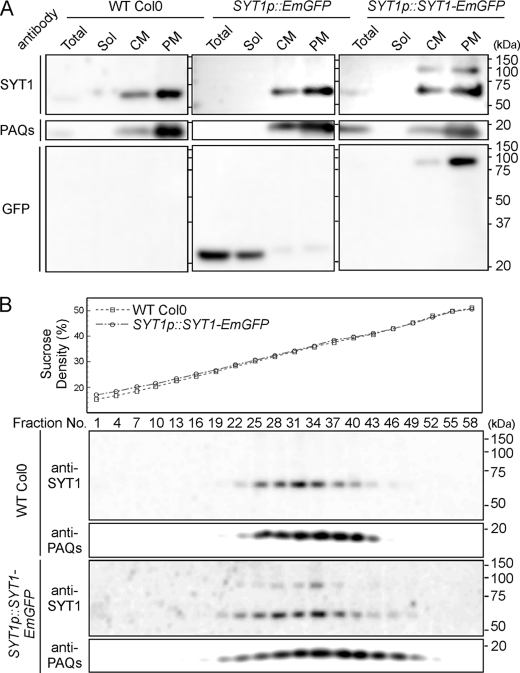
FIGURE 1.
Immunoblot analysis of Arabidopsis plants expressing SYT1-EmGFP. A, purification of crude membrane vesicles. Seedlings of wild-type plants (Col0) and transgenic plants expressing EmGFP or SYT1-EmGFP under the SYT1 promoter (i.e. SYT1p::EmGFP or SYT1p::SYT1-EmGFP) were homogenized, and after centrifugation, supernatants were fractionated (Total) into soluble proteins and crude membrane vesicles. After ultracentrifugation, supernatants containing soluble proteins (Sol) and crude membrane vesicles (CM) were fractionated. From the CM fraction, plasma membrane vesicles (PM) were fractionated by the aqueous two-phase partition system. These fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblot analysis was performed using the anti-SYT1, which recognizes the C2A domain, anti-GFP and anti-PAQs, which recognizes total plasma membrane aquaporin, antibodies. Molecular mass is indicated to the right of the blot. B, separation of crude membrane vesicles from wild-type plants and the two transgenic plant seedlings using linear sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Sucrose densities of each fraction were measured (upper panel), and aliquots of each fraction were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-SYT1 and anti-PAQ antibodies.