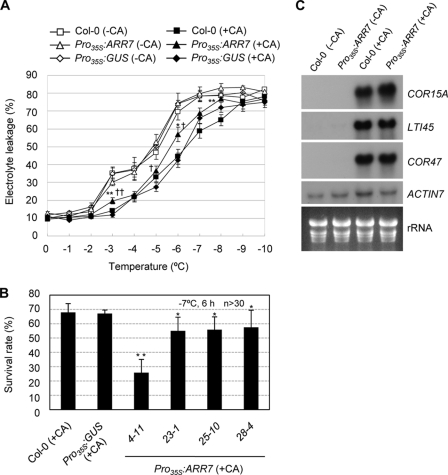
FIGURE 7.
Freezing tolerance assays and RNA-gel blot analysis of Pro35S:ARR7, Pro35S:GUS, and the wild-type plants with or without cold acclimation. A, electrolyte leakage of Pro35S:ARR7 and the wild-type plants with or without cold acclimation. Electrolyte leakage assays were conducted using the leaves from 2-week-old wild-type (Col-0) and Pro35S:ARR7 (line 4-11) (29) plants treated with or without cold acclimation (CA). For cold acclimation treatment, the plants were incubated for 3 days at 1 °C under white fluorescent light. The means ± S.E. from 10 experiments were plotted. Statistically significant changes compared with those of Col-0 plants (or Pro35S:GUS plants) are indicated by * (or †) when p < 0.05 or by ** (or ††) when p < 0.01 (Student's t test), respectively. B, freezing tolerance assays of various lines of Pro35S:ARR7 transgenic Arabidopsis, Pro35S:GUS, and the wild-type plants after cold acclimation. Ten-day-old plants were cold-acclimated at 1 °C for 3 days, treated with −7 °C for 6 h, and photographed after 2 days of incubation at 23 °C for recovery. The percentage of the plants that survived was calculated. The means ± S.E. from four independent experiments were plotted. n ≥30. # indicates line number of Pro35S:ARR7 (29). Statistically significant changes compared with the Col-0 plants as well as Pro35S:GUS plants are indicated by * when p < 0.05 or by ** when p < 0.01 (Student's t test), respectively. C, RNA-gel blot analysis of Pro35S:ARR7 and the wild-type plants. Total RNA was isolated from plants treated with or without cold acclimation and was subjected to RNA-gel blot analysis using the indicated probes. Line 4-11 of Pro35S:ARR7 (29) was utilized.