Figure 3.
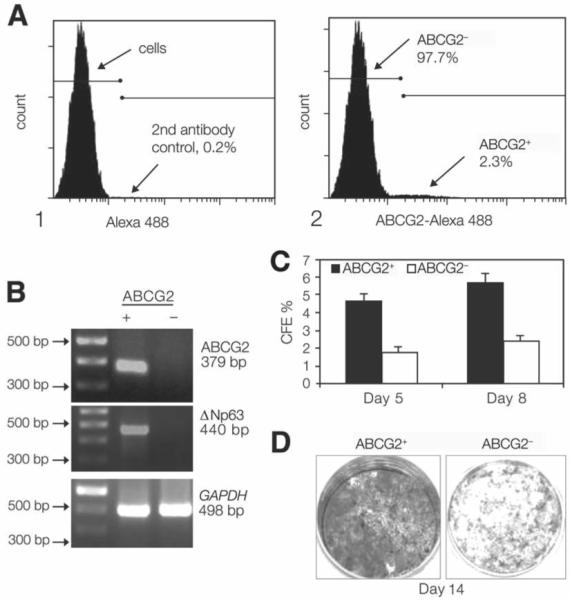
(A): Flow cytometry analysis of cultured human limbal epithelial cells showing a distinctive small population of ABCG2+ cells (2.31%). (B): Semiquantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction showing higher expression of ABCG2 mRNA (379 bp) in the ABCG2+ cells sorted by fluorescence–activated cell sorting. A 100-bp DNA ladder is shown in the first left lane. GAPDH (498 bp), a housekeeping gene, was used as an internal control. (C): CFE of ABCG2-selected populations showing a greater colony-forming efficiency generated by the ABCG2+ cells at days 5 and 8 than that by ABCG2− cells (p < .005 and p < .001, respectively). (D): Growth capacity of ABCG2+ cells and ABCG2− cells, evaluated by 1% rhodamine staining at day 14, showing that ABCG2+ cells were confluent, whereas ABCG2− cells had fewer colonies. Abbreviation: CFE, colony-forming efficiency.
