Table 1.
Acronyms
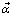 |
ℝN | the dual variable of SVM |
| Q | ℝN × N | a semi-positive definite matrix |
| C | ℝN | a convex set |
| Ω | ℝN × N | a combination of multiple semi-positive definite matrices |
| j | ℕ | the index of kernel matrices |
| p | ℕ | the number of kernel matrices |
| θ | [0, 1] | coefficients of kernel matrices |
| t | [0, + ∞) | dummy variable in optimization problem |
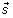 |
ℝp | 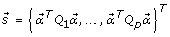 |
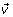 |
ℝp | 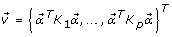 |
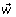 |
ℝD or ℝΦ | the norm vector of the separating hyperplane |
| ϕ(·) | ℝD → ℝΦ | the feature map |
| i | ℕ | the index of training samples |
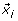 |
ℝD | the vector of the i-th training sample |
| ρ | ℝ | bias term in 1-SVM |
| ν | ℝ+ | regularization term of 1-SVM |
| ξi | ℝ | slack variable for the i-th training sample |
| K | ℝN × N | kernel matrix |
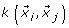 |
ℝD × ℝD → ℝ | kernel function, 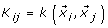
|
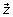 |
ℝD | the vector of a test data sample |
| yi | -1 or +1 | the class label of the i-th training sample |
| Y | ℝN × N | the diagonal matrix of class labels Y = diag(y1, ..., yN) |
| C | ℝ+ | the box constraint on dual variables of SVM |
| b | ℝ+ | the bias term in SVM and LSSVM |
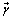 |
ℝp | 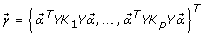 |
| k | ℕ | the number of classes |
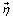 |
ℝp | 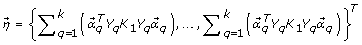 |
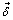 |
ℝp | variable vector in SIP problem |
| u | ℝ | dummy variable in SIP problem |
| q | ℕ | the index of class number in classification problem, q = 1, ..., k |
| A | ℝN × N | 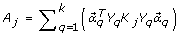 |
| λ | ℝ+ | the regularization parameter in LSSVM |
| ei | ℝ | the error term of the i-th sample in LSSVM |
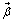 |
ℝN | the dual variable of LSSVM, 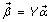
|
| ϵ | ℝ+ | precision value as the stopping criterion of SIP iteration |
| τ | ℕ | index parameter of SIP iterations |
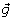 |
ℝp | 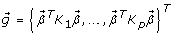 |
