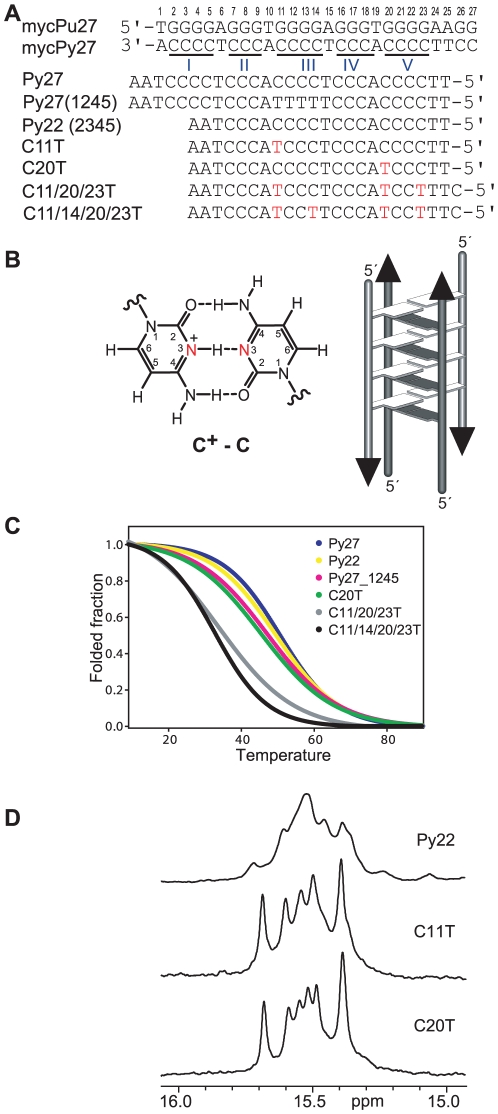
Figure 1. The c-MYC NHE III1 sequences and I-motif structure.
(A) The promoter sequence of the NHE III1 element of the c-MYC gene and its modifications. mycPu27 is the wild-type 27-mer G-rich sequence of the c-MYC NHE III1; Pu22 is the modified G-rich sequence that adopts the single predominant c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex and was used for structure determination [35]; mycPy27 is the wild-type 27-mer C-rich sequence of the c-MYC NHE III1; Py27 is the wild-type C-rich promoter sequence with a 3′-AA; Py27(1245) is the modified Py27 that can only form the (1245) form of the c-MYC I-motif; Py22 is the truncated wild-type Py27 with a 3′-AA that can only form the (2345) form of the c-MYC I-motif; C11T, C20T, C11/20/23T, and C11/14/20/23T are the modified Py22 with single C-to-T substitutions. The numbering system is based on the G-rich strand and is shown above mycPy27. (B) A C+-C base pair (left), and a schematic drawing of a four-stranded I-motif structure (right). (C) CD melting curves of various C-rich c-MYC promoter sequences shown in (A) at pH 5.5. (D) Imino regions of 1D 1H NMR spectra of Py22, C11T, and C20T at 25°C, pH 5.5.