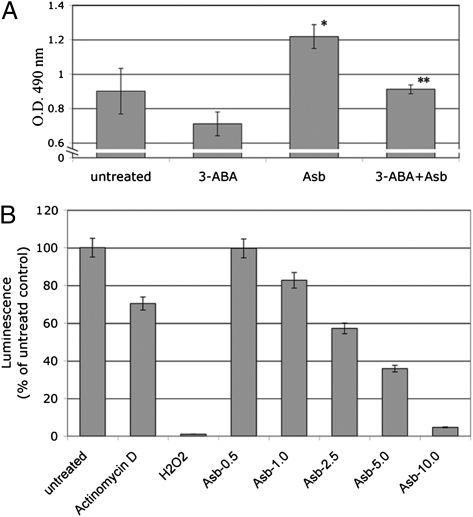
Fig. 2.
Asbestos-induced HM death is PARP dependent and causes ATP depletion. (A) PARP inhibitor 3-ABA decreases asbestos cytotoxicity. HM were incubated with or without 3-ABA (0.5 mM) for 1 h before asbestos exposure (5 μg/cm2). Representative results of three separate experiments are shown. Cytotoxicity was detected using the LDH assay. 3-ABA decreased asbestos cytotoxicity and protected HM from asbestos-induced cell death. *Significantly different compared with HM without asbestos exposure. **Significantly different compared with HM exposed to asbestos without 3-ABA pretreatment (P < 0.05). (B) Asbestos induces ATP depletion in HM. HM were treated with actinomycin D (0.1 μM, positive control for apoptosis), H2O2 (200 μM, positive control for necrosis) or with asbestos (0.5–10 μg/cm2) for 24 h. Cellular ATP was measured by a bioluminescence assay. Increasing amounts of asbestos significantly induced ATP depletion. Each column represents the average of three separate experiments.