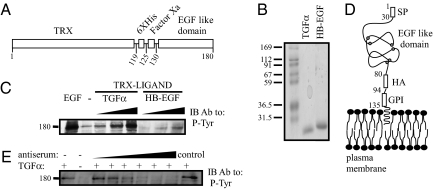
Fig. 1.
Construction, expression and biological activity of recombinant EGF-like ligands. (A) A scheme of an EGF-like chimeric protein, including a thioredoxin (TRX) domain, a histidine box (6XHis), a flanking Factor Xa cleavage site, and a carboxyl-terminal EGF-like domain. Residue numbers are indicated. (B) Coomassie blue staining of an acrylamide gel showing purified TGF-α and HB-EGF prepared using bacterial expression and purified on a NiNTA column. Molecular weight markers are indicated in kilodaltons. (C) Cells were seeded in a 24-well plate, washed, and incubated with increasing concentrations of the purified fusion proteins (TRX–TGF-α: 2, 20, 200 ng/mL; TRX–HB-EGF: 3, 30, 300 ng/mL). EGF (10 ng/mL) was used as a positive control. After a 10-min long incubation, the cells were lysed, and cleared extracts immunoblotted (IB) with an antiphosphotyrosine (P-Tyr) antibody. (D) A scheme presenting the domain structure of a generic GPI-fusion protein comprising the HER2’s signal peptide (SP), the EGF-like domain of TGF-α (or HB-EGF), an HA-peptide tag, and a GPI-lipid anchor. Residue numbers refer to TGF-α. Cysteine residues of the EGF-like domain are highlighted. (E) Cells were seeded in a 24-well plate, washed, and coincubated with or without TGF-α (5 ng/mL), and an antiserum from TGF-α-immunized mice (0.2, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 μL of serum diluted in 120 μL total; control: 10 μL serum from a naive animal). An antiphosphotyrosine mAb was used to detect phosphorylated EGFRs.