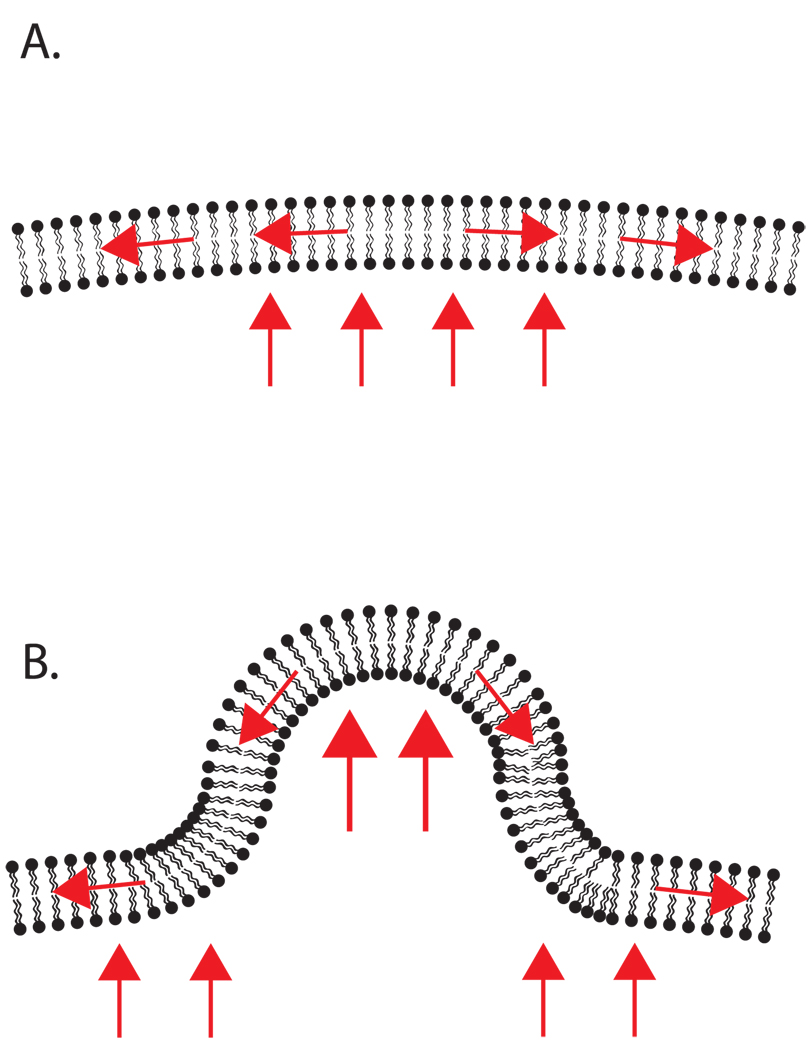
Figure 1.
A simple model of pressure and tension on cell membranes. A. Under steady state conditions, hydrostatic pressure pushing outward is balanced by tension in the membrane. (Red arrows indicate force) B. Shape change is achieved when pressure and tension are imbalanced. In this example, additional local outward pressure leads to protrusion.