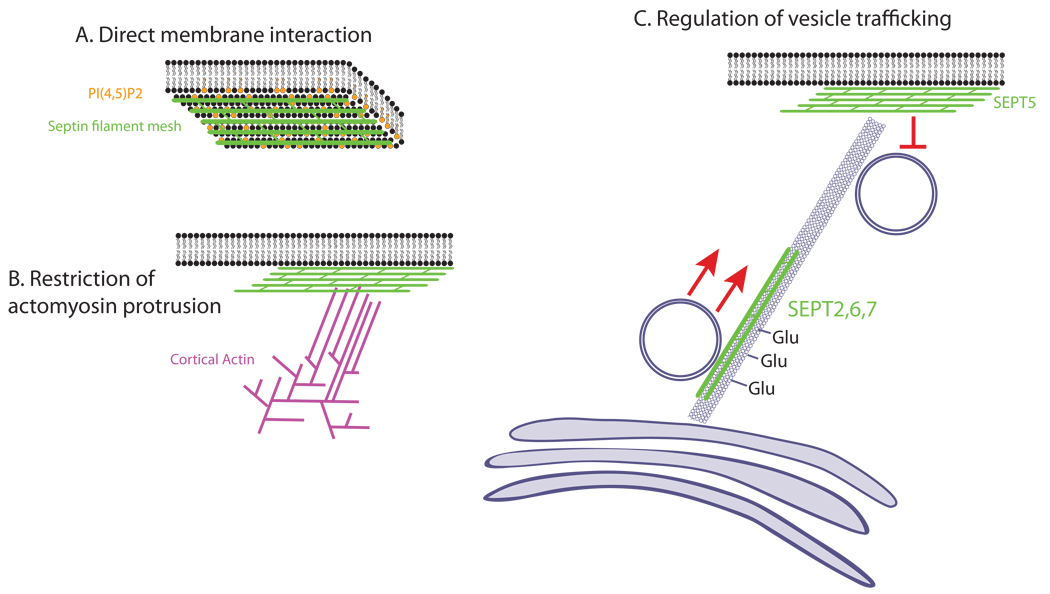
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of cortical control by septins. A. Structural septin meshworks interact directly with membrane lipids to enforce curvature and may provide contacts with the actin cytoskeleton. B. Septins interacting with Myosin II may control actomyosin-mediated protrusions C. Septins can have a positive or negative role in vesicle trafficking, depending on the location and composition of septin complexes. SEPT2-containing filaments line up on polyglutamated microtubules and promote polarized transport. SEPT5-containing filaments are present on the membrane and negatively regulate vesicle docking.