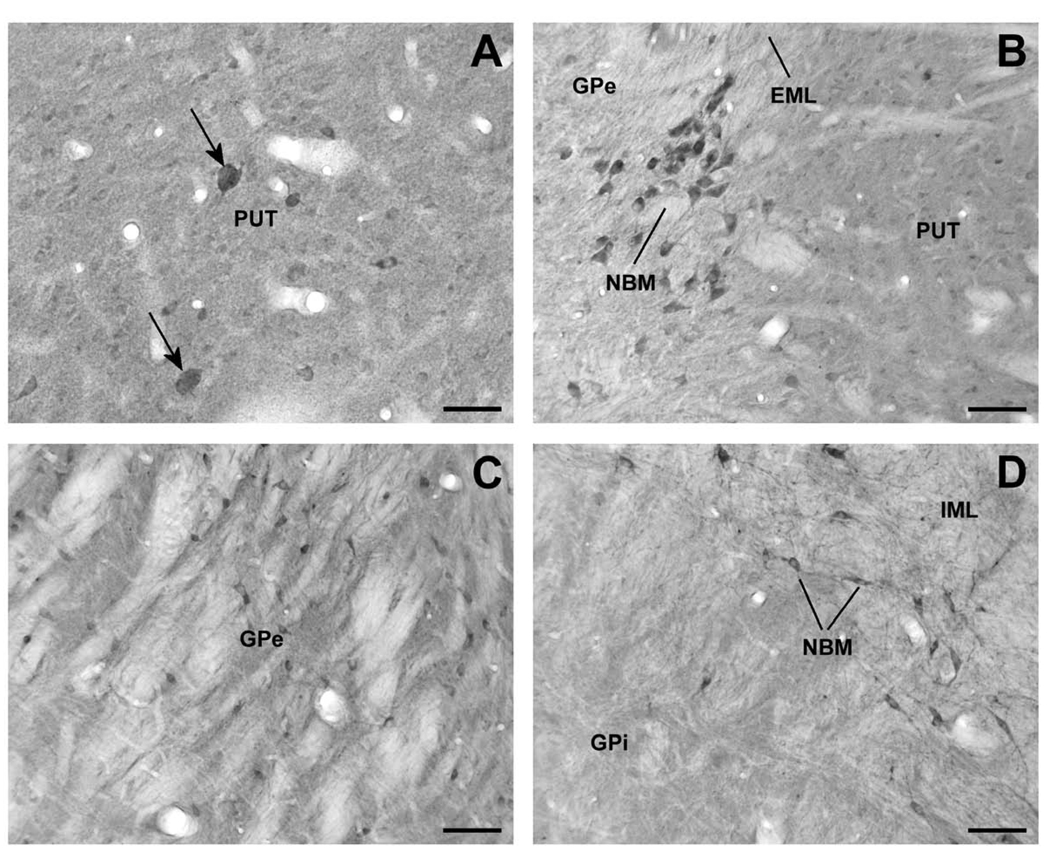
Figure 3.
Lrrk2-immunoreactive elements in the monkey striatopallidal complex and nucleus basalis of Meynert (NBM). (A) High-power micrograph of large cell bodies (arrow) and numerous small Lrrk2-immunoreactive perikarya in the putamen (PUT). (B) A cluster of Lrrk2-immunoreactive neurons that correspond to cholinergic NBM cells lying along the external medullary lamina (EML), between the PUT and GPe. (C) Lrrk2-immunoreactive neuronal profiles in GPe. (D) High magnification micrograph showing a lack of immunoreactive neurons in the internal segment of globus pallidus (GPi) in contrast to strong immunopositive neurons of NBM that lie along the internal medullary lamina (IML). Scale bars = 50 µm (A); 100 µm (B – D).