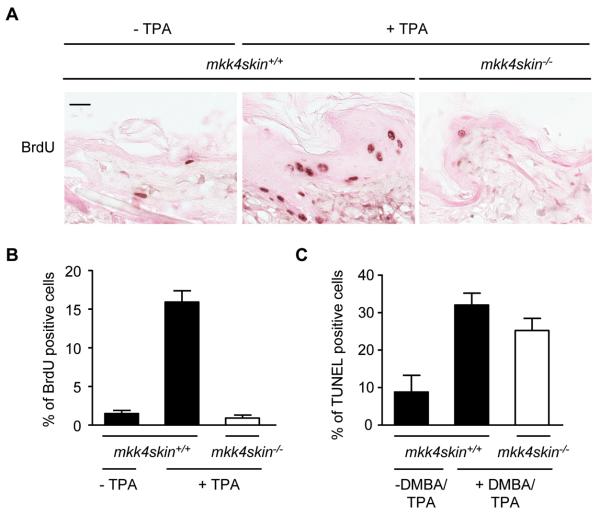
Figure 3.
Lack of MKK4 prevents TPA-induced cell proliferation. A, Dorsal skins of mkk4skin+/+ and mkk4skin−/− mice received a single application of TPA. Controls correspond to age matched untreated mkk4skin+/+ mice. The mice were injected intraperitoneally with BrdU 24 h after TPA treatment. The dorsal skins were isolated 2 h later and processed for BrdU immunoreactivity. Positive cells are stained in brown. B, Quantitative analysis of BrdU-positive cells demonstrates that the number of proliferating cells is higher in the epidermis of mkk4skin+/+ compared to that of mkk4skin−/− animals treated with TPA. C, mkk4skin+/+ and mkk4skin−/− animals were treated with DMBA/TPA for 20 weeks. Controls correspond to age matched untreated mkk4skin+/+ mice. Skin sections were stained by TUNEL. Quantification of TUNEL positive cells indicates no marked difference in the number of apoptotic cells in the epidermis of treated mkk4skin+/+ and mkk4skin−/− mice. The data expressed as percent +/− standard error (SE) were generated from three animals/genotype. 1000 cells per section were counted. Scale bar represents 20 μM.