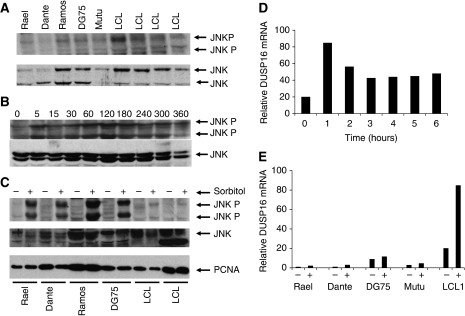
Figure 4.
Methylation in the DUSP16 CpG island modulates inducible but not constitutive activation of JNK via inhibition of negative feedback transcriptional upregulation of DUSP16 expression. (A) Constitutive JNK expression and activity is not elevated in BL relative to LCL and is unrelated to the expression and methylation status of DUSP16. Protein lysates were prepared from exponentially growing BL cell lines and LCL as indicated and JNK expression and activity were determined by western blotting as described in Materials and Methods section. (B) JNK phosphorylation is induced by sorbitol. Ramos BL cells were serum-starved over night, then treated with 0.4 M sorbitol. Cells were collected at the indicated times (min) and total and phosphorylated JNK determined by western blotting as described in Materials and Methods section. JNK phosphorylation is maximal at 120 min after the addition of sorbitol. (C) Sorbitol induces JNK activation in BL but not LCL. The indicated BL cell lines were serum starved overnight then challenged with sorbitol. After 30 min, JNK phosphorylation was determined by western blotting as described in Materials and Methods section. (D) Sorbitol induces transcriptional upregulation of DUSP16. EBV-immortalised lymphoblastoid cells were exposed to 0.4 M sorbitol and DUSP16 mRNA levels determined by qPCR at the indicated times (h) as described in Materials and Methods section. Induced levels of DUSP16 mRNA are maximal at 1 h after addition of sorbitol. Data shown are from a representative experiment. (E) Methylation blocks sorbitol-induced upregulation of DUSP16 mRNA. LCL and BL cell lines, as indicated, were serum-starved overnight, then challenged with 0.4 M sorbitol (+) or not exposed to sorbitol (−). DUSP16 mRNA levels were determined by qPCR after 1 h as described in Materials and Methods section. Data shown are from a representative experiment.