Figure 3.
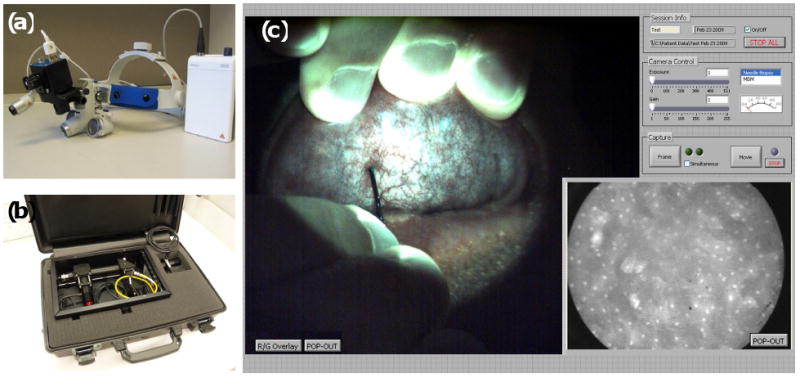
Combined portable widefield and high-resolution imaging systems. (A) The portable screening system weighs only 3 lb. (B) High-resolution microendoscope contained in a briefcase. (C) Widefield and high-resolution images of normal human oral mucosa acquired with the multimodal imaging system. In the widefield image (left frame), the green autofluorescence of normal tissue is apparent, as well as the microvascular network. The high-resolution fiber-optic probe can be seen in contact with the mucosal surface, approaching from the base of the widefield frame. The high-resolution image, acquired simultaneously, is displayed in the lower right frame, with the 800 μm diameter field-of-view corresponding to the tissue located beneath the tip of the fiber-optic probe. Following topical application of 0.05% proflavine solution to the probe tip, nuclei appear as discrete bright regions within each epithelial cell.
