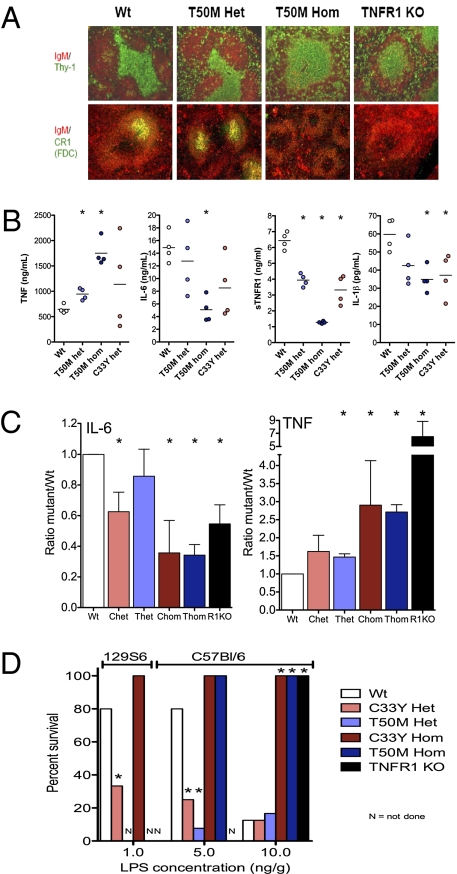
Fig. 3.
Phenotype and altered responsiveness to LPS in knockin mice harboring TRAPS-associated TNFR1 mutations. (A) Immunofluorescence images of the indicated markers in spleens from mice with targeted TNFR1 mutations, performed as previously described (38). Note the lack of well-defined T-cell zones or complement receptor 1 (CR1)-positive follicular dendritic cells in T50M TNFR1 homozygous mutant mice. (B) Serum cytokine concentrations 2 h after i.p. injection with 50 ng/g LPS in mice that were either WT (Wt), heterozygous for T50M mutation (T50M Het), homozygous for T50M mutation (T50M Hom), or heterozygous for the TNFR1 T50MC33Y mutation (C33Y Het). (C) Summary of serum concentrations of IL-6 and TNF 2 h after i.p. LPS injection from seven independent experiments performed as described in B. Ratios are normalized to the average of each cytokine detected in each experiment ± SEM. *, P < 0.05 from t test comparisons vs. WT mice. Chet, heterozygous C33Y; Chom, homozygous C33Y; R1KO, homozygous knockout for TNFR1; Thet, heterozygous T50M; Thom, homozygous T50M. (D) Summary of three independent lethality studies, with survival of mice of the indicated genotype (either 129S6 background or C57BL/6 background) after i.p. injection of the indicated doses of LPS and D-galactosamine. *, P < 0.05 from t test comparisons vs. WT mice.