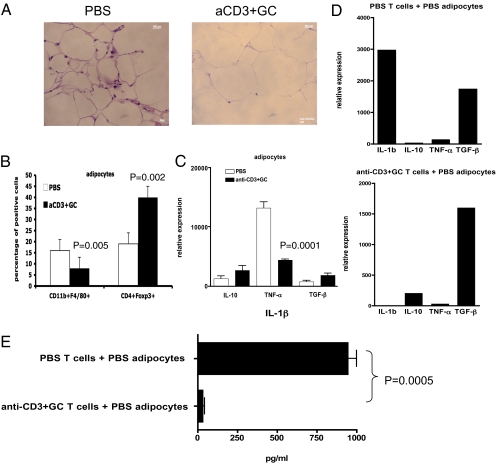
Fig. 5.
Oral anti-CD3 + GC decreases CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages, TNF-α, and IL-1 and increases CD4+Foxp3+ cells in adipose tissue of ob/ob mice. (A) Mice (four per group) were fed PBS or anti-CD3 (5 μg) plus GC (100 μg) for 5 consecutive days. At 72 h after the last feeding, perigonadal white fat was collected and fat paraffin sections were stained with H&E. Pictures were taken at a magnification of ×100. (B) At 72 h after the last feeding (six mice per group), white fat near or surrounding MLNs was used to isolate adipocytes. Adipocytes were stained with fluorescent antibodies to CD11b and F4/80 or CD4 and were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with antibody to Foxp3. aCD3, anti-CD3. (C) At 72 h after the last feeding, RNA of adipocytes isolated from perigonadal fat was used in quantitative RT-PCR for cytokine expression of IL-10, TNF-α, and TGF-β. (D) CD4+ T cells were negatively selected from spleens of PBS- or anti-CD3 + GC-fed mice and cocultured with adipocytes from control mice at a 1:1 ratio for 5 days. CD4+ T cells were eliminated from coculture by positive selection, leaving adipocytes for extraction of RNA used in quantitative RT-PCR for cytokine expression. These experiments were repeated three times with the same results. Error bars represent SD. (E) Culture supernatants were harvested from cocultures of CD4+ T cells from control or anti-CD3 + GC-fed mice and adipocytes of control mice. The amount of IL-1β was measured by ELISA.