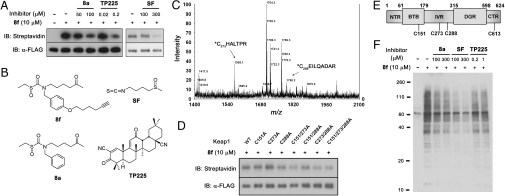
Fig. 4.
Sulfoxythiocarbamate analog conjugates on Keap1 cysteines as well as potential target proteins in cells. (A) Labeling FLAG-Keap1 in cells. HEK293 cells transiently expressing FLAG-tagged Keap1 were treated with 8f for 0.5 h, or pretreated with 8a, sulforaphane, or TP225 for 0.5 h before incubation of 8f for 0.5 h. FLAG-Keap1 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with anti-FLAG antibody, subjected to reaction with biotin azide and eluted with FLAG peptide. Samples were immunoblotted with streptavidin (Top) and anti-FLAG antibody (Bottom). (B) Structure of compounds, 8f, 8a, sulforaphane, and TP225. (C) MALDI-MS spectrum of FLAG-Keap1 tryptic digests labeled by 8f. Eluted FLAG-Keap1 was digested by trypsin, followed by incubation with avidin-coated beads. Biotin-conjugated peptides were eluted with aq. acetonitrile and analyzed by MALDI mass spectrometry, which showed two peaks corresponding to modified Cys 273 and Cys 288 peptides. (D) Labeling FLAG-Keap1 cysteine to alanine mutants. Cells transiently expressing FLAG-tagged WT or mutant Keap1 were treated with 8f for 0.5 h. FLAG-Keap1 proteins, eluted after immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody and conjugation with biotin azide, were immunoblotted with streptavidin (Top) and anti-FLAG antibody (Bottom). (E) Schematic structure of Keap1 with five domains that include NTR, BTB, IVR, DGR, and CTR. Cys 288 and Cys 613 modified peptides were found by LTQ mass analysis. (F) Labeling potential target proteins in cells. After incubation of compounds as described in A, cell lysates were subjected to click reaction with biotin azide, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with streptavidin HRP.