Figure 3.
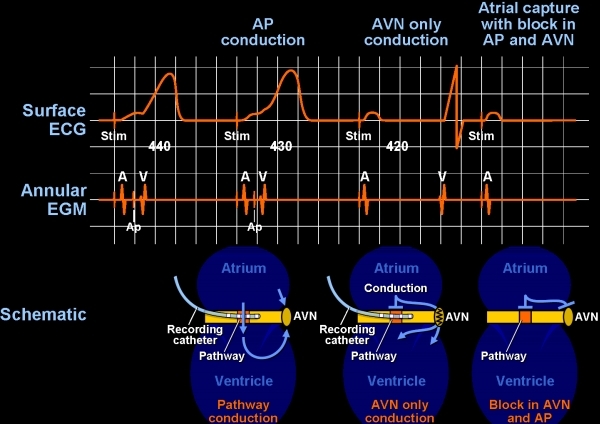
Accurate diagnosis of a candidate potential as an accessory pathway potential is important for any accessory pathway ablation, but it is critical for safe ablation of septal pathways. The suspicious potential in this patient with an antegrade conducting pathway is noted between the atrial (A) and ventricular (B) electrograms. The operator must distinguish the AP potential from a fragmented portion of the atrium or ventricular electrograms. The most important, however, is to make sure this is not part of the atrial electrogram, since targeting such an electrogram will be meaningless. Pacing at a more rapid rate causes block in the accessory pathway and subsequently block in the AV node, as well. The atrial electrogram is seen to be easily dissociated from the accessory pathway potential (Ap) thus ensuring that it was not a fragmented portion of the V. AP = accessory pathway; EGM = electrogram; ECG = electrocardiogram;
