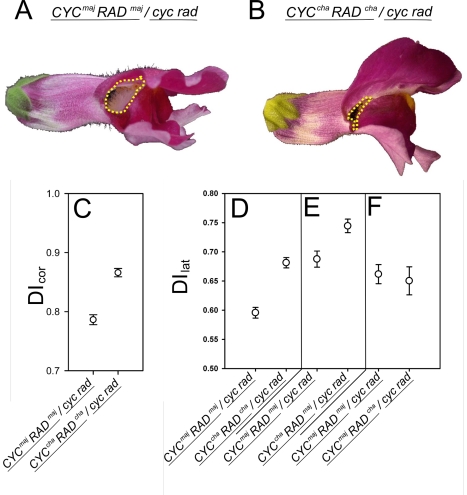
Figure 5. Phenotypes and DI values for introgressed lines.
(A and B) Segregating phenotypes obtained from crossing CYCmajRADmaj/CYCchaRADcha to the double mutant cyc rad/cyc rad. Yellow dotted line shows where the rims of the lateral and dorsal tube meet and highlights the difference between the effect of A. charidemi alleles (left) and those of A. majus (right). (C) DI cor values for the genotypes in (A and B). Note that the A. charidemi alleles give a higher DI cor value than the A. majus alleles (two-sided t-test 114.87df = 7.24, p<0.001). (D) DI lat values for progeny obtained from CYCmajRADmaj/CYCchaRADcha crossed to the double mutant cyc rad/cyc rad. The A. charidemi alleles give a higher DI lat value than the A. majus alleles (two-sided unpaired t-test 508df = 6.73, p<0.001). (E) DI lat values for progeny from a plant heterozygous for a recombinant allele (CYCmajRADmaj/CYCchaRADmaj) crossed to the double mutant cyc rad/cyc rad. Plants carrying the CYCcha allele have a higher DI lat value than those carrying the CYCmaj (two-sided t-test 202.37df = 3.14, p = 0.002). (F) DI lat values for progeny from a plant heterozygous for a recombinant allele (CYCmajRADmaj/CYCmajRADcha) crossed to the double mutant cyc rad/cyc rad. Plants carrying the RADcha allele are not significantly different from those carrying RADmaj (two-sided t-test 202.37df = 3.14, p = 0.002). Bars indicate standard errors.