Fig. 12.
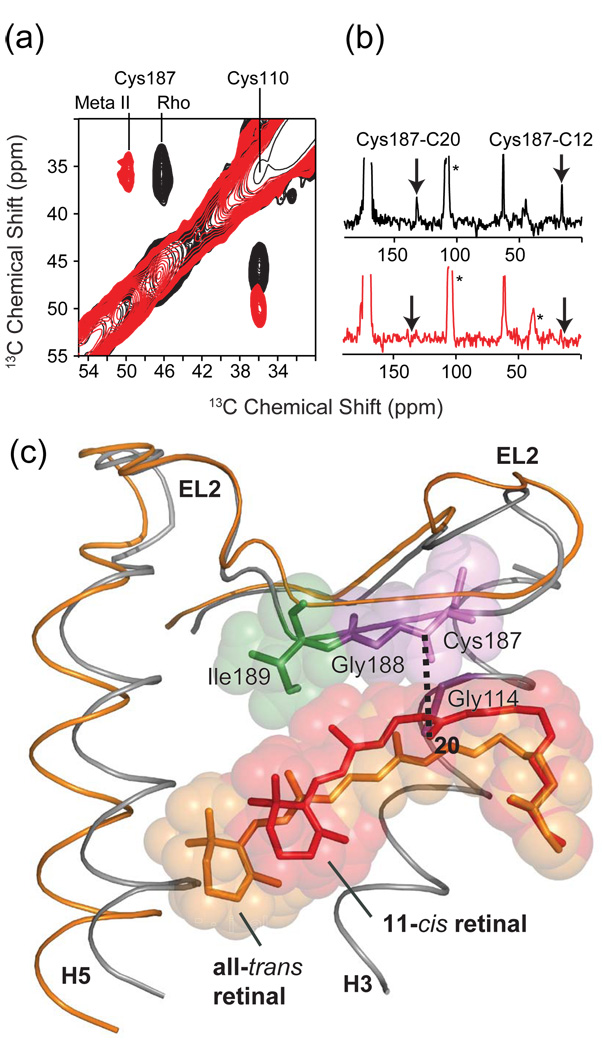
Solid-state NMR chemical shift and dipolar coupling measurements on EL2 in rhodopsin. (a) Chemical shift measurements from 150 MHz 13C 2D DARR NMR spectra of rhodopsin and Meta II showing the shift in the 13Cβ resonance of Cys187 on EL2. The Cys110 – Cys187 disulfide bond is conserved in the Class A GPCRs. The 13Cβ chemical shifts of disulfide linked cysteines are shifted by ~25 ppm from those of reduced cysteines. The chemical shift of Cys110 of ~36 ppm is characteristic of a cysteine in α-helical secondary structure, while the chemical shift of Cys187 between 46 ppm and 50 ppm is characteristic of extend β-structure. (b) Dipolar coupling measurements from 2D NMR spectra of rhodopsin (top) and Meta II (bottom) showing the loss of retinal-EL2 contacts upon the formation of Meta II. (c) Overlay of the crystal structure of rhodopsin and the structure of Meta II developed on the basis of NMR measurements and MD simulations [106]. EL2 is displaced from the retinal-binding pocket in the active Meta II state. The figure is adapted from Ref. [106].