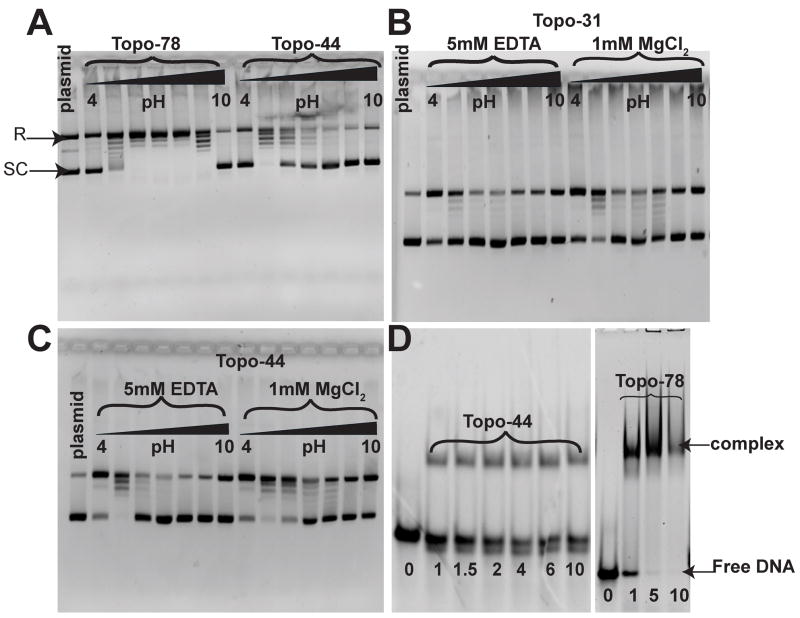
Figure 2. DNA relaxation activity and EMSA for Topo-31, Topo-44 and Topo-78 fragments of topoisomerase V.
A) pH profile of the DNA relaxation activity of Topo-78 and Topo-44 fragments. 0.2 μg of pUC19 DNA were incubated with 0.1 μg of Topo-78 or 1.5 μg of Topo-44 proteins at 65°C for 15 minutes for the relaxation reaction. The reaction buffer contained 50 mM of the appropriate buffer, 30 mM NaCl and 0.2 mM EDTA. Topo-78 relaxes DNA at a wider pH range (5 to 9) than Topo-44, which relaxes DNA efficiently only at pH 5. DNA relaxation activity of Topo-31 (B) and Topo-44 (C) fragments in the absence and presence of MgCl2. 0.2 μg of pUC19 DNA were incubated with 9 μg of Topo-31 or 1.5 μg of Topo-44 proteins at 65°C for 15 minutes for the relaxation reaction. The reaction buffer contained 50 mM of the appropriate buffer, 30 mM NaCl and 5 mM EDTA or 1 mM MgCl2. Both Topo-31 and Topo-44 fragments can relax DNA in the absence of MgCl2, but MgCl2 enhances the DNA relaxation activity of the topoisomerase V fragments. The black triangle in panels A, B and C represents increasing pH from 4 to 10 by one pH unit. D) EMSA of Topo-44 and Topo-78 fragments with a 39mer double stranded DNA. Both Topo-44 and Topo-78 form stable complexes with DNA, although Topo-78 seems to saturate DNA binding while Topo-44 does not. In addition, Topo-44 shows some cleavage of the DNA (bottom free DNA band), while the cleavage is not apparent in Topo-78. The numbers at the bottom represent the molar ratio of protein to DNA.