Figure 1.
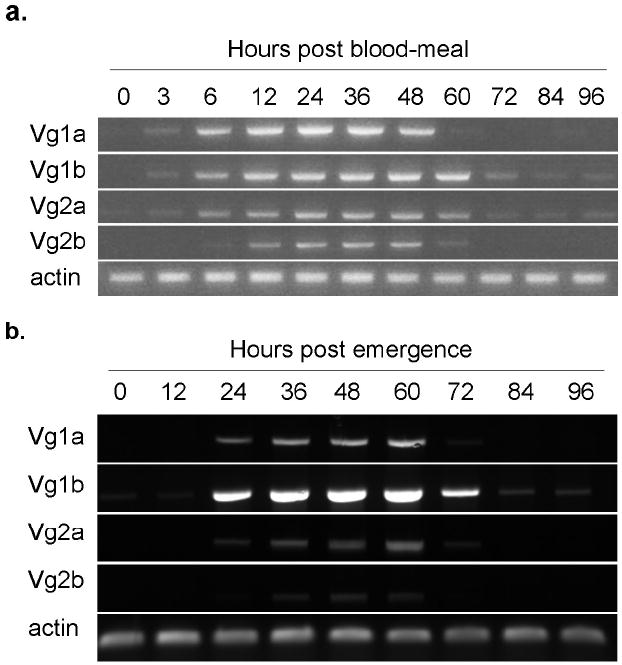
a. Expression of the four vitellogenin genes following a blood meal in KNWR-au. Females of the KNWR-au strain were allowed to emerge and deposit their autogenous egg raft before blood feeding. RNA for cDNA synthesis was extracted from groups of 10 females collected pre-blood meal (PBM) and at indicated time points following blood feeding out to 96 hours. RT-PCR was performed using primers specific to each of the four Culex tarsalis vitellogenin genes (Vg1a, Vg1b, Vg2a, Vg2b) and actin to control for RNA quality.
b. Expression of the four vitellogenin genes during autogenous ovarian development in KNWR-au. RNA for cDNA synthesis was extracted from groups of 10 females collected at indicated time points (0h and every 12 hours out to 96 hours) following eclosion from the pupal stage. RT-PCR was performed using primers specific to each of the four Culex tarsalis vitellogenin genes (Vg1a, Vg1b, Vg2a, Vg2b) and actin to control for RNA quality.
