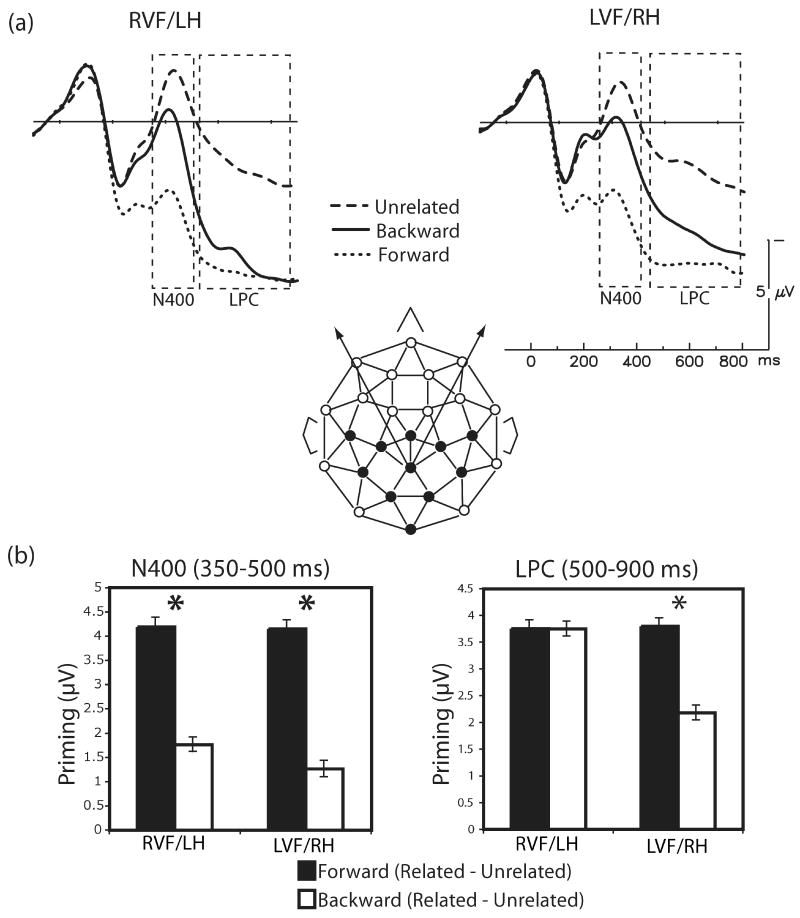
Figure 3.
(a) Grand average ERPs to targets in the forward, backward and unrelated pairs at a representative channel (MiPa), with RVF/LH targets plotted on the left and LVF/RH targets plotted on the right. In both VFs, N400 amplitudes (350 to 500 ms) were sensitive to associative strength, with the smallest N400s to the strongly associated forward pairs and weaker (but significant) priming for the weakly associated backward pairs, as compared with unrelated targets. LPC amplitudes (500 to 900 ms) were modulated by associative strength for LVF/RH targets, but not for RVF/LH targets, which showed equal priming for forward and backward pairs. (b) In both VFs, there was greater N400 priming for forward pairs than backward pairs, and no difference in N400 effect sizes across VF. LPC priming tracked patterns of N400 priming for LVF/RH targets, but LPC priming for both forward and backward targets in the RVF/LH was indistinguishable and comparable to that seen for LVF/RH forward targets.