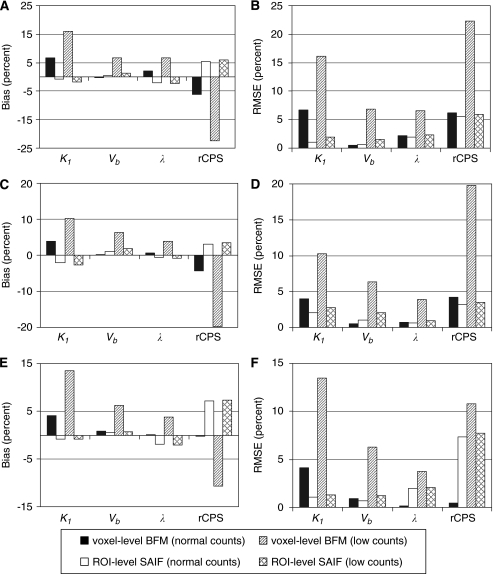
Figure 3.
Bias% and root mean square error (RMSE)% for multiple-voxel region of interest (ROI) simulation. Shown are the simulated central slices of the frontal cortex (A and B), thalamus (C and D), and corona radiata (E and F). Parameter estimates were computed in two ways: using basis function method (BFM) at the simulated voxel level and averaging the parameter estimates over all voxels within the ROI (voxel-level BFM), and using spectral analysis with iterative filter (SAIF) to fit the simulated ROI TAC (ROI-level SAIF). Normal count rate simulations were based on data measured in one subject administered 25.9 mCi [11C]leucine (peak scanner count rate 3.4 × 106 counts per second). Low count rate simulations used blood input functions 25% of the measured values. At normal count rates, performance of the two analysis methods was similar. At low count rates, performance of the voxelwise estimation method worsened while changes in ROI-level SAIF performance were minimal.