Figure 7.
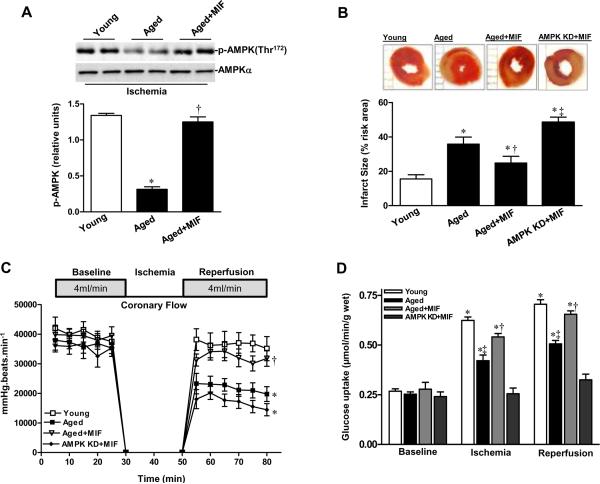
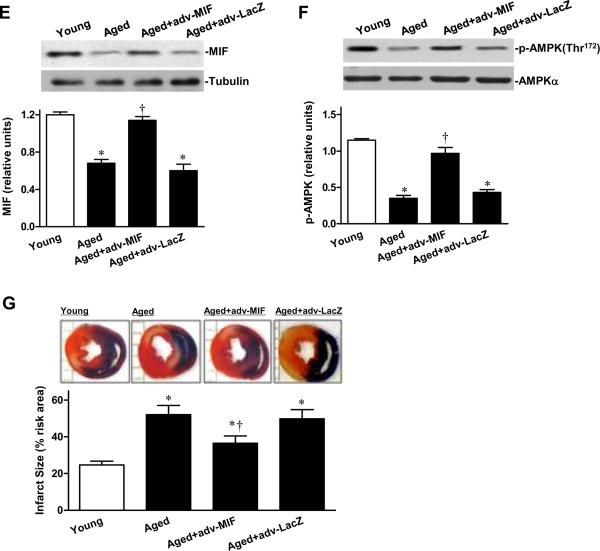
Supplemental MIF restores ischemic AMPK signaling in aged heart. A, Phosphorylation of AMPK in isolated young and aged hearts pretreated with or without MIF (10 ng/mL) during ex vivo global ischemia, n=4 per group, *P=0.01 vs. young; †P=0.01 vs. aged. B, The percent of infarct size to area-at-risk of isolated young, aged and AMPK KD hearts subjected to ex vivo global ischemia (20 min)/reperfusion (2 hr), n=4 per group. *P<0.05 vs. young, respectively; †P=0.03 vs. aged; ‡P=0.01 vs. aged+MIF. C, The heart rate-left ventricular pressure products of isolated young, aged and AMPK KD hearts with or without MIF treatment, n=4 per group, *P<0.05 vs. young, respectively; †P=0.01 vs. aged. D, Glucose uptake under baseline, ischemia and reperfusion in hearts from young, aged and AMPK KD mice supplemented with or without recombinant MIF, n=5 per group. *P<0.05 vs. baseline, respectively; ‡P<0.05 vs. young ischemia or reperfusion, respectively; †P<0.05 vs. aged ischemia or reperfusion, respectively. E, The expression levels of cardiac MIF (upper panel). Bars represent the relative levels of MIF protein (lower panel), n=4 per group, *P<0.05 vs. young, respectively; †P=0.01 vs. aged. F, Phosphorylation of AMPK in ischemic area of young, aged, and aged hearts with intra-myocardial adv-MIF during in vivo regional ischemia (20 min), n=4 per group, *P<0.05 vs. young, respectively; †P=0.01 vs. aged. G, The percent of infarct size to area-at-risk of young, aged and aged hearts with adv-MIF or adv-LacZ treatment, all were subjected to in vivo regional ischemia (20 min)/reperfusion (4 hr) (upper panel). Bars represent the percent of infarct size to area-at-risk (lower panel), n=5 per group, *P<0.05 vs. young, respectively; †P=0.02 vs. aged.