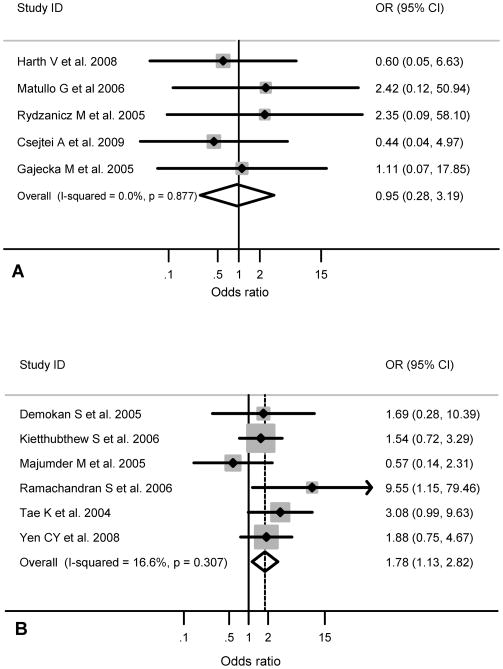
Figure 2.
(A) Published case-control studies show non-significant association of the XRCC1 exon 6 codon 194 (T/T) homozygous variant and the risk of head and neck cancer Caucasian populations. The shaded boxes represent the study-specific odds ratio, and the horizontal lines represent the confidence intervals; the size of the boxes depict how each study is weighted in the analysis, the diamond represents the meta-OR and its width represents the CI for the meta-OR. (B) Published case-control studies show a significant association of the XRCC1 exon 6 codon 194 (T/T) homozygous variant and the risk of head and neck cancer Asian populations. The shaded boxes represent the study-specific odds ratio, and the horizontal lines represent the confidence intervals; the size of the boxes depict how each study is weighted in the analysis, the diamond represents the meta-OR and its width represents the CI for the meta-OR.